SAB4200071
ANTI-FLAG® antibody, Rat monoclonal
clone 6F7, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Synonyme(s) :
Anti-ddddk, Anti-dykddddk
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
rat
Conjugué
unconjugated
Forme d'anticorps
purified from hybridoma cell culture
purified immunoglobulin
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
6F7, monoclonal
Forme
buffered aqueous solution
Espèces réactives
all
Technique(s)
immunoprecipitation (IP): 2.5-5.0 μg using lysates of transiently transfected cells expressing C-terminal-FLAG-tagged protein
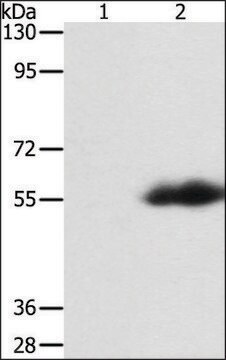
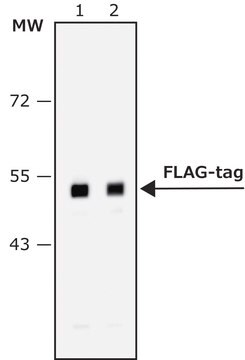
western blot: 0.5-1.0 μg/mL using extracts of transiently transfected cells expressing C-terminal-FLAG-tagged protein
Isotype
IgG1
Séquence immunogène
(DYKDDDDK)
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Description générale
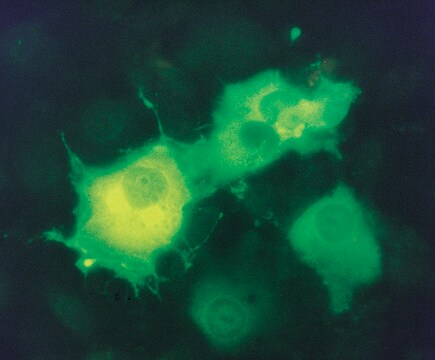
Monoclonal Anti-FLAG® recognizes N-terminal,
C-terminal and internal Flag-tagged fusion proteins. The product is especially recommended for identifying C-terminal FLAG®-tagged fusion proteins.
Epitope tags provide a method to localize gene products in a variety of cell types, study the topology of proteins and protein complexes, identify associated proteins, and characterize newly identified, low abundance, or poorly immunogenic proteins when protein specific antibodies are not available. Tagging with the FLAG® peptide sequence may be done at the N-terminus, N-terminus preceded by a methionine residue, C-terminus, or at internal positions of the target protein. FLAG may also be placed in associationith other tags. The small size of the FLAG® tag or sequence and its high hydrophilicity tend to decrease the possibility of interference with the protein expression, proteolytic maturation, antigenicity, and function.
The N-terminal FLAG® peptide sequence contains a unique enterokinase cleavage site allowing it to be completely removed from the purified fusion proteins. Cleavage of the C-terminal FLAG® peptide from a fusion protein catalyzed by Cu2+ ions has been reported. A sequence motif with five out of eight amino acid residues identical to the FLAG peptide is found in both rat and mouse Mg2+dependent protein b-phosphatase, as well as in the human and bovine enzyme.
Immunogène
DYKDDDDK
Application
- chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
- western blotting
- coimmunoprecipitation
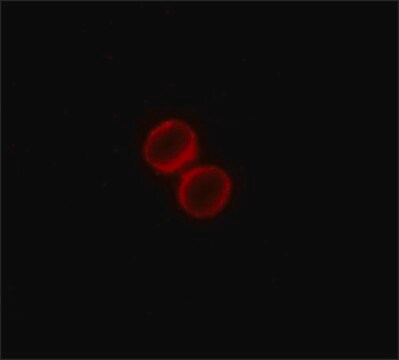
- flow cytometric analysis
Forme physique
Informations légales
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique