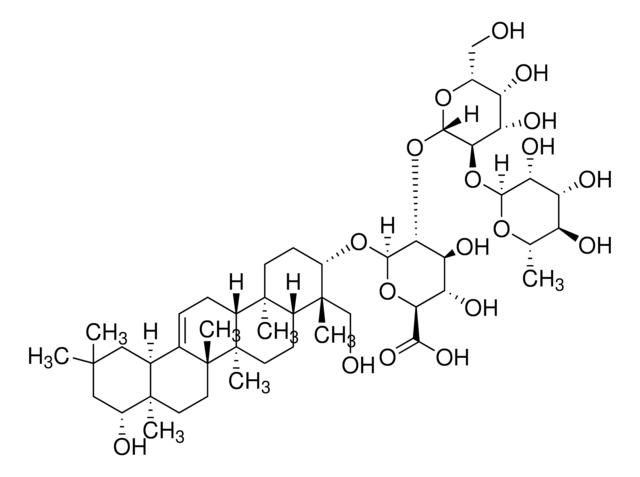
S4521
Saponin from Quillaja sp.
Sapogenin content 20-35 %
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Numéro CAS:
Numéro CE :
Numéro MDL:
Code UNSPSC :
12161902
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.32
Produits recommandés
Description
non-ionic
Niveau de qualité
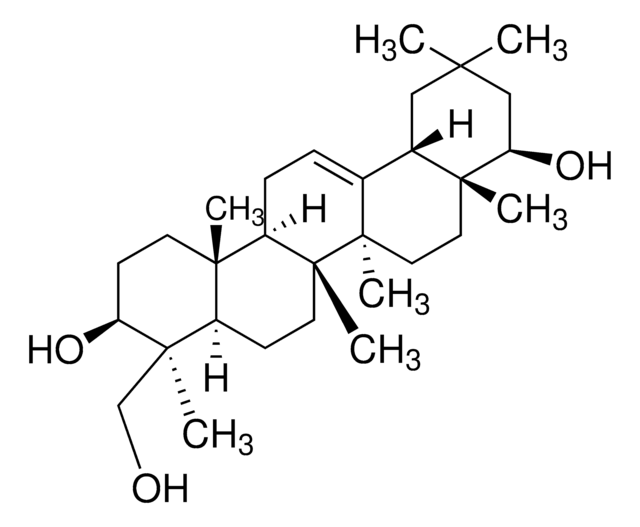
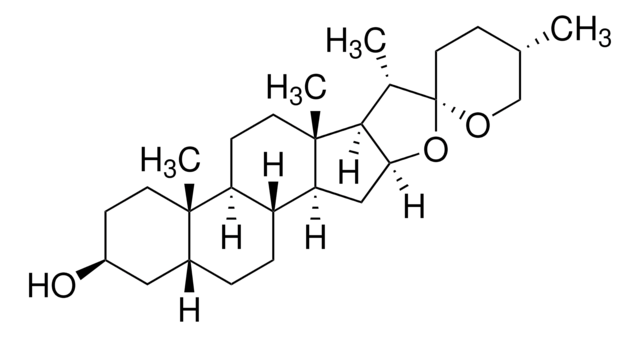
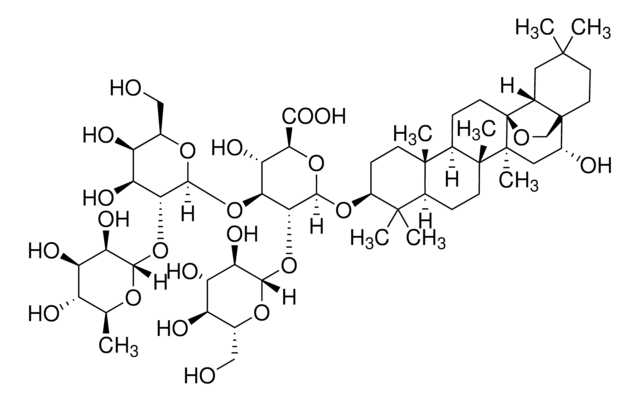
Composition
Sapogenin content, 20-35%
Technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
protein quantification: suitable
Cendres sulfatées
≤10%
Description générale
Saponins are steroid or triterpenoid glycosides. They are biosurfactants that have several uses in the food and cosmetic industry.
Application
Saponin from Quillaja bark has been used:
- to stain fertilized oocytes
- in the analysis of intracellular cytokine production
- to permeabilize dendritic cells
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Saponins solubilize the low density lipoprotein (LDL) fraction of cholesterol in micelles, thus lowering their concentration. Saponin from Quillaja bark is used as a flavoring agent in food and beverages. This saponin has been shown to enhance immune-cell proliferation in vitro.
Potent hemolytic when injected i.v.; surfactant that enhances penetration of proteins and other macromolecules through cell membranes; it also has been used as an adjuvant for vaccines.
Notes préparatoires
Purified to remove low molecular weight contaminants
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organes cibles
Respiratory system
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Subset-dependent modulation of dendritic cell activity by circovirus type 2.
Vincent IE
Immunology, 115(3), 388-398 (2005)
Isolation of myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells from human bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.
Tsoumakidou M
Immunology and Cell Biology, 84(3), 267-273 (2006)
Dynamic chromatin modifications characterise the first cell cycle in mouse embryos.
Santos F
Developmental Biology, 280(1), 225-236 (2005)
Yvonne Lange et al.
Biochemistry, 48(36), 8505-8515 (2009-08-07)
A few membrane-intercalating amphipaths have been observed to stimulate the interaction of cholesterol with cholesterol oxidase, saponin and cyclodextrin, presumably by displacing cholesterol laterally from its phospholipid complexes. We now report that this effect, referred to as cholesterol activation, occurs
Adjuvant effects of saponins on animal immune responses.
Rajput ZI
Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B, 8(3), 153-161 (2007)
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique