RAB0372
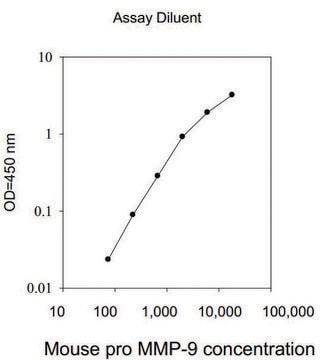
Human MMP-9 ELISA Kit
for serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant and urine
Synonyme(s) :
MMP-9, Matrix metalloproteinase-9
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Code UNSPSC :
41116158
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.32
Produits recommandés
Espèces réactives
human
Conditionnement
kit of 96 wells (12 strips x 8 wells)
Technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
capture ELISA: suitable
Entrée
sample type serum
sample type cell culture supernatant(s)
sample type plasma
Méthode de détection
colorimetric
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Informations sur le gène
human ... MMP9(4318)
Description générale
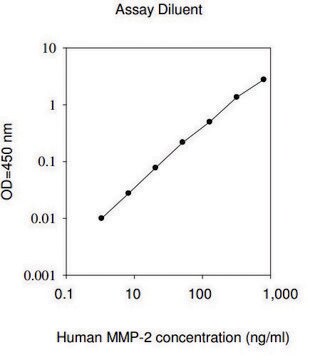
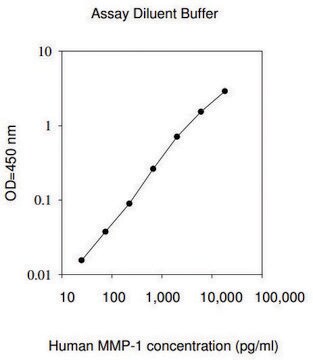
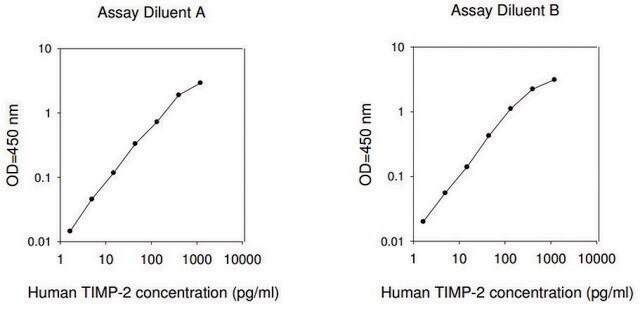
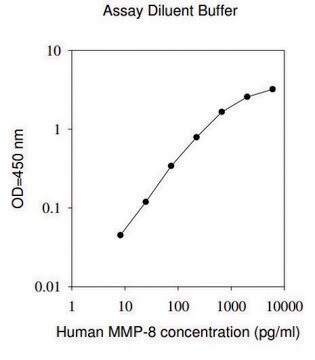
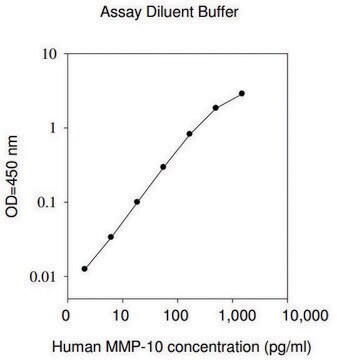
The Human MMP-9 ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative measurement of human MMP-9 pro and active forms in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine.
Immunogène
Recombinant Human MMP9
Application
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) is a gelatinase enzyme, which catalyzes the degradation of gelatin and collagen and is preferentially inhibited by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1). The MMP9 protein is a zinc-dependent protease which is responsible for degradation of extracellular matrix components. It also participates in the pathogenesis of cancers. MMP9 is associated with various disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, acute lung injury, asthma as well as respiratory syncytial virus infection both in vitro and in vivo. MMP-9 is involved in a variety of autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis and be regarded as a potential therapeutic target. Mutation of MMP-9 is associated with lumbar-disc herniation (LDH) and metaphyseal anadysplasia (MAD).
Autres remarques
A sample Certificate of Analysis is available for this product.
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Met. Corr. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Elevated circulatory MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels and activities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Chang YH
Clinical Biochemistry null
A functional polymorphism in THBS2 that affects alternative splicing and MMP binding is associated with lumbar-disc herniation.
Hirose Y
American Journal of Human Genetics null
Mutations in MMP9 and MMP13 determine the mode of inheritance and the clinical spectrum of metaphyseal anadysplasia.
Lausch E
American Journal of Human Genetics null
Elevated concentrations of serum matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and their associations with circulating markers of cardiovascular diseases in chronic arsenic-exposed individuals.
Islam MS
Environmental Health : A Global Access Science Source null
Somanath Kundu et al.
MedChemComm, 8(12), 2248-2257 (2018-08-16)
Bile acids have emerged as strong signaling molecules capable of influencing various biological processes like inflammation, apoptosis, cancer progression and atherosclerosis depending on their chemistry. In the present study, we investigated the effect of major hydrophobic bile acids lithocholic acid
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique