L2898
Lysostaphine from Staphylococcus staphylolyticus
aseptically filled
Synonyme(s) :
Glycyl-glycine endopeptidase
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Stérilité
aseptically filled
Niveau de qualité
Forme
powder
Activité spécifique
>500 units/mg protein
Poids mol.
25 kDa
Composition
Protein, 40-70% biuret
Spectre d'activité de l'antibiotique
Gram-positive bacteria
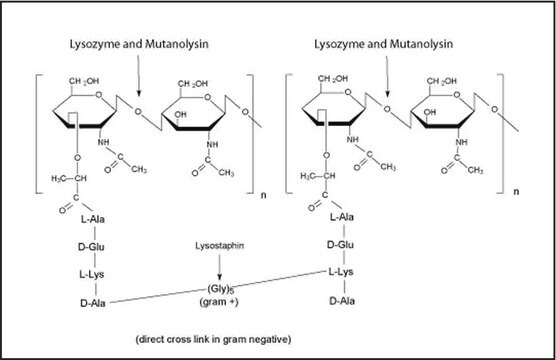
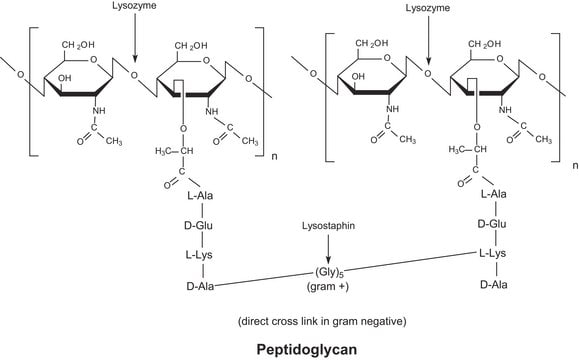
Mode d’action
cell wall synthesis | interferes
Température de stockage
−20°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
pH optimal en termes d'activité : ~7,5
Définition de l'unité
Notes préparatoires
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Resp. Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique