H5529
Heregulin-α, EGF Domain human
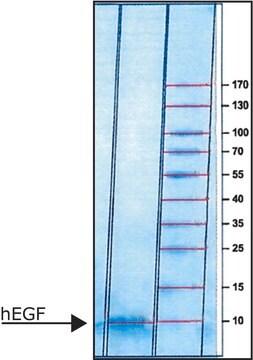
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell culture, ≥97% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonyme(s) :
HRG-α
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
human
Niveau de qualité
Produit recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Essai
≥97% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
lyophilized powder
Puissance
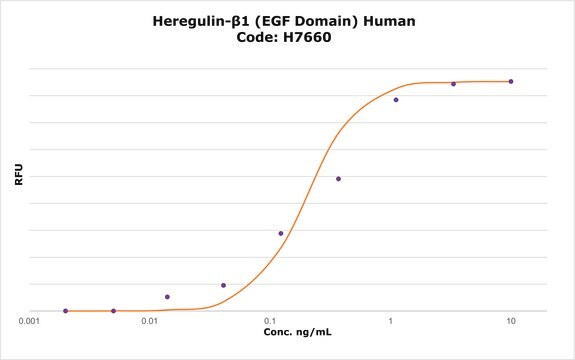
10-50 ng/mL
Poids mol.
protein 8 kDa (reducing conditions)
protein ~7 kDa (predicted)
Conditionnement
pkg of 50 μg
Technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Impuretés
endotoxin, tested
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Température de stockage
−20°C
Informations sur le gène
human ... NRG1(3084)
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Heregulin (HRG) is the human homologue to the neu differentiation factor (NDF) in rat. HRGs inhibit proliferation and induce differentation in tumor cell lines, such as mammary tumor cells. HRGs also induce expression of acetylcholine receptors and other molecules in muscle cells at newly formed neuromuscular synapses, suggesting they may play a role in neuromuscular synapse maturation and maintenance.
Heregulin (HRG) is the human homologue to the neu differentiation factor (NDF) in rat. The heregulin family members contain one EGF-like motif and an IgD-like motif in the extracellular domain. They bind to ErbB-2, ErbB-3, and ErbB-4 (receptors closely related to EGFR). HRG-α and HRG-β isoforms differ slightly in the EGF domain due to alternate splicing. HRG-β isoforms are further subdivided into β1, β2, and β3 isoforms, which show identical binding and activation characteristics. Both α and β HRG isoforms bind to ErbB-3 and ErbB-4 homodimers, but not directly to ErbB-2. HRG-α binding to ErbB-3 and ErbB-4 is reported to be approximately 100-fold weaker than that of HRG-β. When ErbB-2 is combined into a heterodimer with ErbB-3 or ErbB-4, the binding affinities of both α and β isoforms are substantially improved. HRGs are mitogenic for Schwann cells in culture and weakly to moderately mitogenic for a variety of epithelial cells, including mammary, ovarian, lung, and gastric cells. HRGs inhibit proliferation and induce differentation in some tumor cell lines, such as certain mammary tumor cells, which are arrested at the G2M phase. HRGs also induce expression of acetylcholine receptors and possibly other molecules in muscle cells at newly formed neuromuscular synapses, suggesting they may play a role in neuromuscular synapse maturation and maintenance.
Forme physique
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 50 μg bovine serum albumin per 1 μg as a carrier protein.
Remarque sur l'analyse
The bioactivity is tested in culture using a proliferation assay with the human cell line MCF-7.
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
J T Jones et al.
FEBS letters, 447(2-3), 227-231 (1999-04-24)
ErbB receptor activation is a complex process and is dependent upon the type and number of receptors expressed on a given cell. Previous studies with defined combinations of ErbB receptors expressed in mammalian cells have helped elucidate specific biological responses
Z Aguilar et al.
Oncogene, 18(44), 6050-6062 (1999-11-11)
The heregulins are a family of ligands with ability to induce phosphorylation of the p185HER-2/neu receptor. Various investigators have reported a variety of responses of mouse and human breast and ovarian cells to this family of ligands including growth stimulation
S Y Baek et al.
Developmental neuroscience, 20(6), 512-517 (1998-12-22)
Neu differentiation factor (NDF), a 44-kD polypeptide, is a member of the neuregulin family which also includes glial growth factor, heregulin and acetylcholine-receptor-inducing activity. Previous studies have demonstrated that NDF/glial growth factor/heregulin/acetylcholine-receptor-including activity are products of neurons and mediate proliferation
Neu differentiation factor (NDF) and the neuregulin (NRG) family.
Yarden, Y., Wen, D. et al.
The Cytokine Handbook, 146-146 (1998)
Take your partners, please--signal diversification by the erbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases.
R J Daly
Growth factors (Chur, Switzerland), 16(4), 255-263 (1999-07-31)
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique