E1895
Erlose
≥94% (HPLC)
Synonyme(s) :
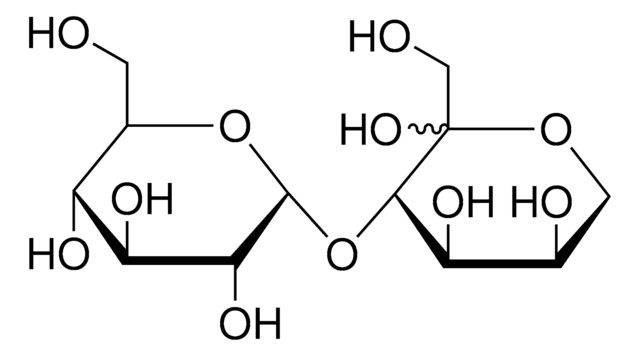
α-D-Glc-(1→4)-α-D-Glc-(1→2)-β-D-Fru, α-Maltosyl β-fructofuranoside
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
plant
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
≥94% (HPLC)
Forme
powder
Activité optique
[α]20/D 108.5 to 112.0 °, c = 0.84% (w/v) in water
Conditions de stockage
desiccated
Impuretés
≤12.5% water (Karl Fischer)
Couleur
white to off-white
Solubilité
H2O: 50 mg/mL, clear to slightly hazy, colorless to faintly yellow
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[C@@H]2CO)O[C@]3(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O
InChI
1S/C18H32O16/c19-1-5-8(23)10(25)12(27)16(30-5)32-14-7(3-21)31-17(13(28)11(14)26)34-18(4-22)15(29)9(24)6(2-20)33-18/h5-17,19-29H,1-4H2/t5-,6-,7-,8-,9-,10+,11-,12-,13-,14-,15+,16-,17-,18+/m1/s1
Clé InChI
FVVCFHXLWDDRHG-KKNDGLDKSA-N
Application
Attention
Autres remarques
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique