C9301
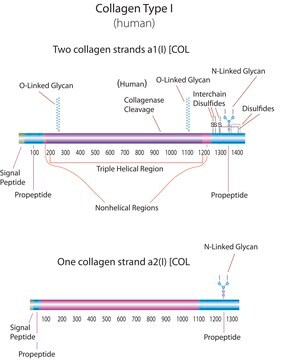
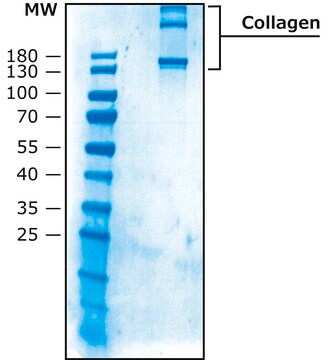
Chicken Collagen Type II
from chicken sternal cartilage, powder, suitable for cell culture
About This Item
Produits recommandés
product name
Collagen from chicken sternal cartilage, Type II (Miller), powder, BioReagent, suitable for cell culture
Source biologique
chicken (Sternal cartilage)
Niveau de qualité
Type
Type II (Miller)
Gamme de produits
BioReagent
Forme
powder
Conditionnement
glass bottle of 100 mg
poly bottle of 25 mg
glass bottle of 5 mg
Concentration
60-80% (biuret)
Technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Couverture de surface
6‑10 μg/cm2
Solubilité
acetic acid: 0.5-2.0 mg/mL (Dissolve for several hours at 2-8 °C, occasionally swirling.)
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Spécificité de la liaison
Peptide Source: Fibrinogen
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Informations sur le gène
chicken ... COL2A1(395069)
Description générale
Application
- in enzyme–linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
- chondrocyte-mediated tissue production in vitro.
- induction, treatment, and assessment of collagenα induced arthritis (CIA).
- cell proliferation assay.
- as a coating for cell culture surfaces.
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Caractéristiques et avantages
Autres remarques
Notes préparatoires
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Cancer stem cell media, spheroid plates and cancer stem cell markers to culture and characterize CSC populations.
Cancer stem cell media, spheroid plates and cancer stem cell markers to culture and characterize CSC populations.
Extracellular matrix proteins such as laminin, collagen, and fibronectin can be used as cell attachment substrates in cell culture.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique