C1744
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase microbial
≥5.0 unit/mg solid
Synonyme(s) :
PEPC
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Forme
lyophilized powder
Activité spécifique
≥5.0 unit/mg solid
Poids mol.
~390 kDa
Température de stockage
−20°C
Application
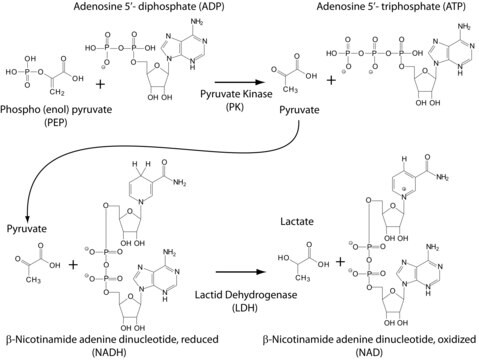
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) is an enzyme useful for enzymatic determination of carbon dioxide when coupled with malate dehydrogenase in clinical analysis. PEPC is also used to study carbon assimilation, post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation in various plants .
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
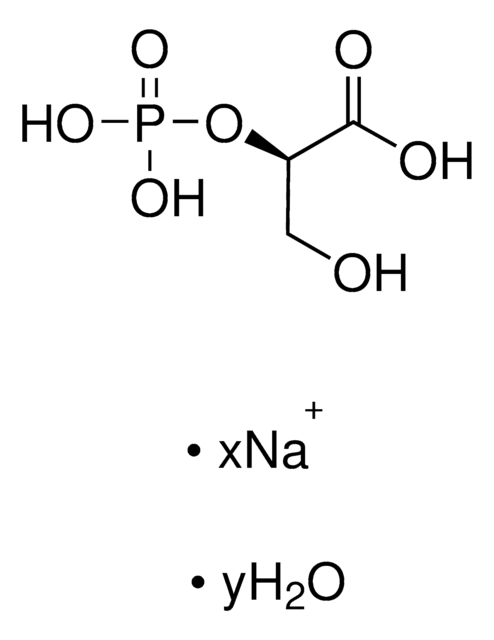
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) catalyzes the addition of bicarbonate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to form the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate and inorganic phosphate . In CAM and C4 plants, PEPC catalyzes the photosynthetic assimilation of CO2 into an organic acid. PEPC is activated by glucose-6-phosphate and is inhibited by malate and aspartate. PEPC comprises about 0.5-2% of the soluble protein in alfalfa and soybean nodules .
Définition de l'unité
One unit causes the oxidation of one micromole of NADH per minute at pH 8.0 at 30°C.
Forme physique
White amorphous lyophilized powder containing BSA and sugar alchohols as stabilizers.
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Resp. Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Mika Nomura et al.
Plant & cell physiology, 47(5), 613-621 (2006-03-10)
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC, EC 4.1.1.31) is believed to play a significant role in supporting nitrogen fixation via anaplerotic CO2 fixation for recycling carbon in nodules. Using the antisense technique, we decreased the expression levels of the nodule-enhanced PEPC gene (Ljpepc1)
Masataka Wakayama et al.
Journal of plant research, 126(2), 233-241 (2012-10-18)
The C(4) grass Arundinella hirta exhibits a unique C(4) anatomy, with isolated Kranz cells (distinctive cells) and C(4)-type expression of photosynthetic enzymes in the leaf sheath and stem as well as in the leaf blade. The border zones between these
Patrizia De Nisi et al.
Plant physiology and biochemistry : PPB, 57, 168-174 (2012-06-19)
The regulation exerted by the Fe status in the plant on Fe deficiency responses was investigated in Cucumis sativus L. roots at both biochemical and molecular levels. Besides the two activities strictly correlated with Fe deficiency response, those of the
Jitender Singh et al.
Gene, 500(2), 224-231 (2012-06-20)
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase is an ubiquitous cytosolic enzyme that catalyzes the ß-carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and is encoded by multigene family in plants. It plays an important role in carbon economy of plants by assimilating CO2 into organic acids for subsequent
Judith Katharina Paulus et al.
Nature communications, 4, 1518-1518 (2013-02-28)
The C4-photosynthetic carbon cycle is an elaborated addition to the classical C3-photosynthetic pathway, which improves solar conversion efficiency. The key enzyme in this pathway, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, has evolved from an ancestral non-photosynthetic C3 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. During evolution, C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique