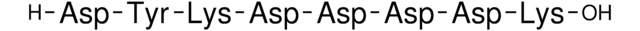A2220
Gel d'affinité ANTI-FLAG® M2
purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous glycerol solution
Synonyme(s) :
Anticorps monoclonal ANTI-FLAG® M2 antibody produced in mouse, Gel d'agarose pour chromatographie d'affinité ANTI-FLAG® M2, Anti-ddddk, Anti-dykddddk
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Conjugué
agarose conjugate
Niveau de qualité
Forme d'anticorps
purified immunoglobulin
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
M2, monoclonal
Forme
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
Classe(s) chimique(s) de l'analyte
proteins
Technique(s)
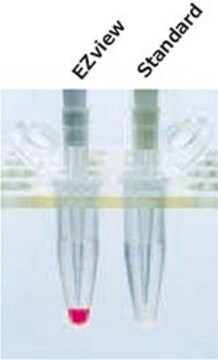
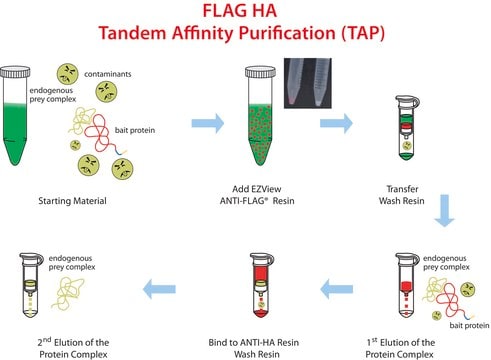
affinity chromatography: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
Matrice
(4% agarose bead; 45-165μm bead size)
Isotype
IgG1
Capacité
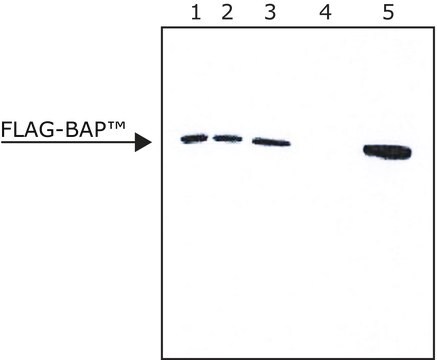
>0.6 mg/mL, resin binding capacity (FLAG-BAP)
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Élution - peptide FLAG®, glycine, pH 3,5, 3x peptide FLAG®
Immunogène
Application
Pour en savoir plus sur nos produits, rendez-vous sur notre portail des applications des produits FLAG®.
Forme physique
Autres remarques
Informations légales
Clause de non-responsabilité
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Souvent commandé avec ce produit
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Contenu apparenté
Protein purification techniques, reagents, and protocols for purifying recombinant proteins using methods including, ion-exchange, size-exclusion, and protein affinity chromatography.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique