MTOX1301Z
MDCKII canine MDR1 KO Cells
Synonyme(s) :
Canine cell line
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
canine kidney (cocker spaniel)
Utilisation
sufficient for 1 96-well plate(s) (or 24-well plate)
Conditionnement
vial of 2 million cells
Mode de croissance
adherent
Technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
drug transporter assay: suitable
Application(s)
ADME/TOX
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Température de stockage
−196°C
Description générale
Application
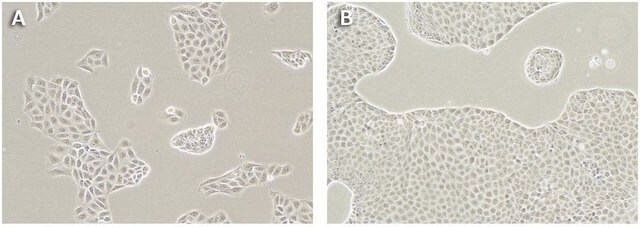
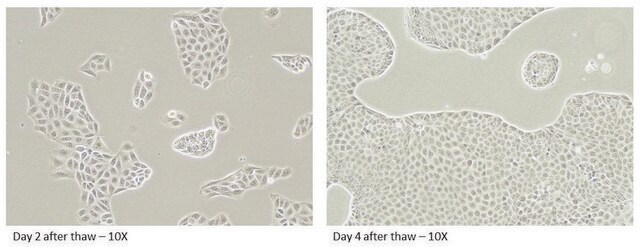
These cells can be used in transwell permeability assays to measure the movement of substrates through the monolayer. Efflux ratios for test compounds can be determined using standard compounds as controls.
Caractéristiques et avantages
The canine MDR1 (cP-gp) efflux transporter gene has been effectively disrupted in both alleles. There is no expression of the cP-gp. Validation studies have shown no efflux of standard cP-gp substrates.
Qualité
Informations légales
MDCKII subclone was originally isolated by Daniel Louvard, Institut Curie, Paris France.
References: Hansson, G.G., Simons, K and Van Meer G (1986) EMBO 5: 483-489, Louvard D (1980) PNAS 77; 4132-4136
En option
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique