MAB8702
Anti-Dengue Virus Type II Antibody, clone 3H5-1
clone 3H5-1, Chemicon®, from mouse
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Code UNSPSC :
12352203
eCl@ss :
32160702
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.41
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
mouse
Niveau de qualité
Forme d'anticorps
purified immunoglobulin
Clone
3H5-1, monoclonal
Espèces réactives
human
Fabricant/nom de marque
Chemicon®
Technique(s)
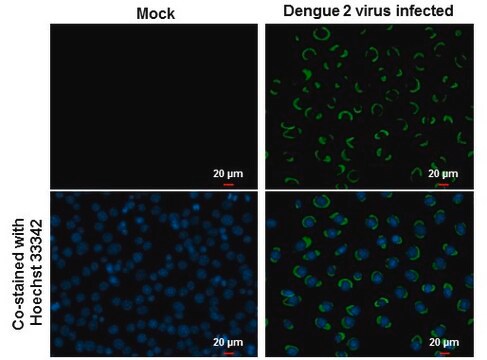
immunofluorescence: suitable
inhibition assay: suitable (hemagglutination)
Isotype
IgG1
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Description générale
Dengue fever is an acute, mosquito-transmitted viral disease characterized by fever, headache, arthralgia (severe retro-orbital pain), myalgia, rash, nausea, and vomiting. Infections are caused by any of the four closely related, but antigenically distinct virus serotypes (DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, and DEN-4). Infection with one of these serotypes does not provide cross-protective immunity, so persons living in a dengue-endemic area can have four dengue infections during their lifetimes. Dengue is primarily an urban disease of the tropics, and the viruses that cause it are maintained in a cycle that involves humans and Aedes aegypti, a domestic, day-biting mosquito that prefers to feed on humans. Although most dengue infections result in relatively mild illness, some can produce Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) or dengue shock syndrome, with children being particularly at risk. Although epidemic outbreaks have been reported since 1779, the incidence has been increasing, with global, multiple serotype pandemics intensifying within the last 15 years. There is no specific antiviral therapy for dengue, but for both classical dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever, symptomatic and supportive measures are effective. Important risk factors for DHF include the strain and serotype of the virus involved, as well as the age, immune status, and genetic predisposition of the patient.
Spécificité
Reacts with the Dengue type 2 virus.
Immunogène
Dengue type 2 antigen (New Guinea C).
Application
Recommended for use in an immunofluorescent assay. Also suitable for use in hemagglutination-inhibition tests and plaque-reduction assays.
IFA: 1:200-1:400.
Dilute with buffer pH 7.5-8.0 to desired working volumes. For extensive dilution, protein containing or other stabilizing medium should be used.
Final working dilutions must be determined by end user.
IFA: 1:200-1:400.
Dilute with buffer pH 7.5-8.0 to desired working volumes. For extensive dilution, protein containing or other stabilizing medium should be used.
Final working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Research Category
Infectious Diseases
Infectious Diseases
Research Sub Category
Infectious Diseases - Viral
Infectious Diseases - Viral
This Anti-Dengue Virus Type II Antibody, clone 3H5-1 is validated for use in HI, IF for the detection of Dengue Virus Type II.
Forme physique
Format: Purified
Protein G Purified
Protein G Purified immunoglobulin. Liquid in 0.02 M PB, 0.25 M NaCl, pH = 7.6 with 0.1% Na Azide as a preservative
Stockage et stabilité
Maintain at 2°C to 8°C in undiluted aliquots for up to 12 months after date of receipt.
Remarque sur l'analyse
Control
Dengue positive patient sample
Dengue positive patient sample
Autres remarques
Concentration: Please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for the lot-specific concentration.
Informations légales
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Clause de non-responsabilité
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Characterization of the early events in dengue virus cell entry by biochemical assays and single-virus tracking.
van der Schaar, HM; Rust, MJ; Waarts, BL; van der Ende-Metselaar, H; Kuhn, RJ; Wilschut et al.
Journal of virology null
Leticia Franco et al.
PLoS neglected tropical diseases, 5(8), e1251-e1251 (2011-08-11)
Dengue virus (DENV) circulates in human and sylvatic cycles. Sylvatic strains are both ecologically and evolutionarily distinct from endemic viruses. Although sylvatic dengue cycles occur in West African countries and Malaysia, only a few cases of mild human disease caused
Hilde M van der Schaar et al.
PLoS pathogens, 4(12), e1000244-e1000244 (2008-12-20)
Dengue virus (DENV) is an enveloped RNA virus that causes the most common arthropod-borne infection worldwide. The mechanism by which DENV infects the host cell remains unclear. In this work, we used live-cell imaging and single-virus tracking to investigate the
Tine De Burghgraeve et al.
PloS one, 7(5), e37244-e37244 (2012-05-25)
There is an urgent need for potent inhibitors of dengue virus (DENV) replication for the treatment and/or prophylaxis of infections with this virus. We here report on an aglycon analogue of the antibiotic teicoplanin (code name LCTA-949) that inhibits DENV-induced
Zhi-Shan Zhang et al.
Molecular medicine reports, 11(2), 1009-1016 (2014-11-06)
There is currently no effective vaccine to prevent dengue infection, despite the existence of multiple studies on potential methods of immunization. The aim of the present study was to explore the effect of DNA and/or recombinant protein on levels of
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique