MAB5596
Anti-HCN2 Antibody
culture supernatant, Chemicon®
Synonyme(s) :
Hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 2
About This Item
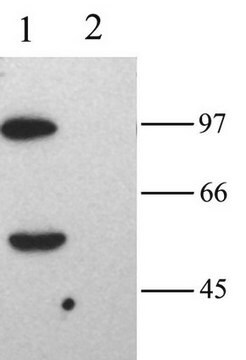
WB
western blot: suitable
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
rat
Niveau de qualité
Forme d'anticorps
culture supernatant
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
monoclonal
Espèces réactives
mouse, rat
Fabricant/nom de marque
Chemicon®
Technique(s)
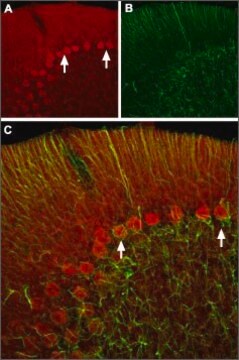
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
Isotype
IgG1
Numéro d'accès NCBI
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Modification post-traductionnelle de la cible
unmodified
Informations sur le gène
mouse ... Hcn2(15166)
rat ... Hcn2(114244)
Spécificité
Immunogène
Application
Neuroscience
Ion Channels & Transporters
Immunohistochemistry on rat and mouse retina.
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Forme physique
Stockage et stabilité
Informations légales
Clause de non-responsabilité
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique