MAB3424
Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AH4H7-1 / 131-14871
Chemicon®, from mouse
Synonyme(s) :
BrdU
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
mouse
Niveau de qualité
Forme d'anticorps
purified immunoglobulin
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
131-14871, monoclonal
AH4H7-1, monoclonal
Réactivité de l'espèce (prédite par homologie)
all
Fabricant/nom de marque
Chemicon®
Technique(s)
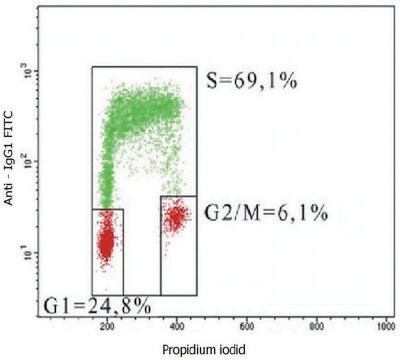
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
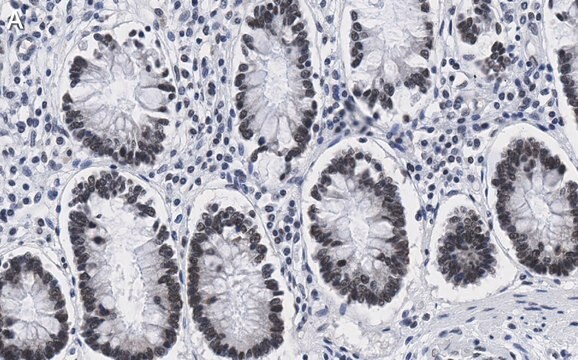
immunohistochemistry: suitable
Isotype
IgG1
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Modification post-traductionnelle de la cible
unmodified
Description générale
Spécificité
Immunogène
Application
Flow Cytometry: (0.2 μg/100 μl/10E6 cells) Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
APPLICATIONS
Flow cytometry:The method below is based on that of M. Vanderlaan et al. (1986). Variations of this method exist in the literature, one consideration being the effect various fixation procedures have on the light-scattering properties of different cell populations. Procedure:
1. To label cells, pulse with 10 μM bromodeoxyuridine for 30 minutes. Harvest cells from culture.
2. Fix cells in 70% ethanol at +2-8°C for at least 30 min. Extract histones by resuspending cells in 1 mL chilled 0.1 M HCI containing 0.5% Triton X-100; incubate the suspension on ice for 10 minutes. Dilute acid with 5 mL distilled water and centrifuge at 200 x g for 10 min. Resuspend cells in 2 mL distilled water.
3. Denature cellular DNA by submerging the cell suspension into a boiling water bath for 10 min. Afterwards, quickly cool by placing the cell suspension in an ice slurry for several minutes. Wash cells in PBS that contains 0.5% Triton X-100.
4. Resuspend the cells (1-2 x 10 6 cells) in 100 μL of solution containing approximately 2 μg/mL anti-bromodeoxyuridine antibody diluted in PBS containing 0.1% BSA (0.2 μg/test). Incubate for 30 min at room temperature. Wash cells with PBS.
5. Resuspend cells in 100 μL of diluted goat anti-mouse IgG-FlTC Wash cells with PBS.
APPLICATIONS (Cont.)
Immunohistochemistry: Below is a procedure for staining cells that have been labeled with BrdU in vivo or in vitro. The procedure is based on the methods of B. Schutte et al. (1987) and D. Campana et al. (1988).
Preparation of tissue:
Inject animal with 50 mg BrdU/kg body weight. Sacrifice animal one hour later and remove organ or tissue under study. Embed tissue in OCT medium and snap-freeze by immersion into liquid nitrogen.Cut 4 mm frozen sections with a cryostat. Place sections on either albumin- or gelatin-coated slides.
Preparation of cells:
Pulse cells with 10 mM BrdU for 60 min. Cells grown on coverslips, or cytocentrifuge preparations made from cells grown in suspension, can be used for anti-bromodeoxyuridine staining according to the procedure below.
Procedure
1. Fix tissue sections or cells (on slide or coverglass) by immersing in absolute methanol for 10 minutes at +2-8°C. Air dry after removing from fixative. The slides can be stored at -20°C in a sealed box, or rehydrated to prepare for the assay procedure. To rehydrate, immerse in PBS for 3 min.
2. Denature DNA by incubating the slides in 2 N HCI for 60 min at +37°C.
3. Neutralize the acid by immersing the slides in 0.1 M borate buffer, pH 8.5. Change the buffer twice over a 10 min period.
4. Wash slides with PBS, changing the solution three times over a 10 min period.
5. Place slides in a humidified chamber (e.g., a sealed plastic box layered with wet paper towels) and cover cells with 150-300 μL of solution containing approximately 6 μg/mL anti-bromodeoxyuridine antibody diluted in PBS with 0.1% BSA. Incubate for 60 min at room temperature.
6. Wash slides with PBS, changing the solution three times over a 10 min period.
7. Apply optimal dilution of a second antibody conjugate (e.g., anti-mouse IgG-peroxidase), incubate, wash, and perform detection with a substrate that produces an insoluble product. After detection, counterstain with Harris-modified hematoxylin if desired. Slides can then be dehydrated and mounted.
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Cell Cycle, DNA Replication & Repair
Description de la cible
Liaison
Forme physique
Stockage et stabilité
Remarque sur l'analyse
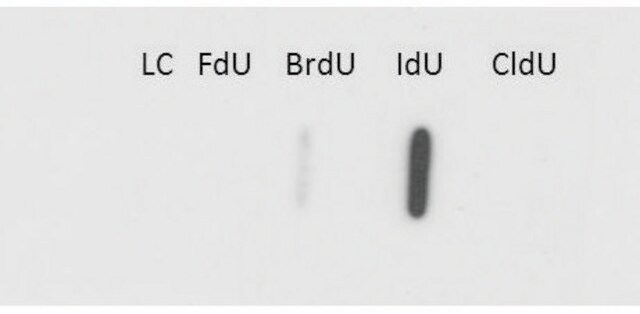
After incorporation of BrdU, all DNA containing species
Autres remarques
Informations légales
Clause de non-responsabilité
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique