208733
Calpain Inhibitor Set
The Calpain Inhibitor Set controls the biological activity of Calpain. This small molecule/inhibitor is primarily used for Protease Inhibitors applications.
Synonyme(s) :
Calplain inhibitor
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Code UNSPSC :
12352200
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.77
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Forme
solid
Puissance
8 nM Ki
Fabricant/nom de marque
Calbiochem®
Conditions de stockage
OK to freeze
desiccated
protect from light
Conditions d'expédition
ambient
Température de stockage
−20°C
Description générale
Calpains are a family of calcium-dependent thiol-proteases that act on a wide variety of cytoskeletal, membrane-associated, and regulatory proteins. There are two major isoforms: calpain I (µ-form) and calpain II (m-form), which differ in their calcium requirement for activation Calpains are composed of heterodimers of 80 kDa and a 30 kDa subunits. The 80 kDa unit has the catalytic site and is unique to each isozyme, whereas the 30 kDa unit is the regulatory subunit and is common to both µ- and m-isozymes.
More recently, attention has been focused on the pathological significance of calcium accumulation in the central nervous system following cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury. Over-activation of NMDA, kainate, and AMPA receptors in the brain leads to sustained influx of Ca2+ through the voltage-gated calcium channels. Overexpression of calpains has been positively linked to both acute and chronic neurodegenerative processes including ischemia, trauma, and Alzheimer′s disease. In Alzheimer′s disease the ratio of active (76 kDa) to inactive (80 kDa) µ-calpain is reported to be much higher Calpain-dependent proteolysis is usually the late-stage common pathway towards cell death induced by excitotoxic compounds, hence, a selective inhibition of calpains to limit neuronal damage appears to be a viable therapeutic measure.
More recently, attention has been focused on the pathological significance of calcium accumulation in the central nervous system following cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury. Over-activation of NMDA, kainate, and AMPA receptors in the brain leads to sustained influx of Ca2+ through the voltage-gated calcium channels. Overexpression of calpains has been positively linked to both acute and chronic neurodegenerative processes including ischemia, trauma, and Alzheimer′s disease. In Alzheimer′s disease the ratio of active (76 kDa) to inactive (80 kDa) µ-calpain is reported to be much higher Calpain-dependent proteolysis is usually the late-stage common pathway towards cell death induced by excitotoxic compounds, hence, a selective inhibition of calpains to limit neuronal damage appears to be a viable therapeutic measure.
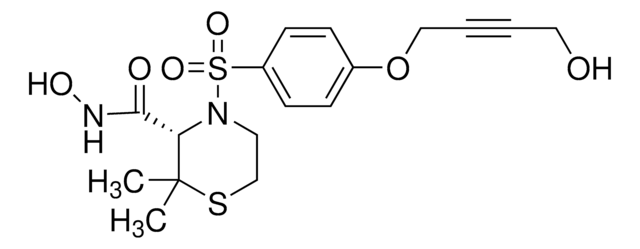
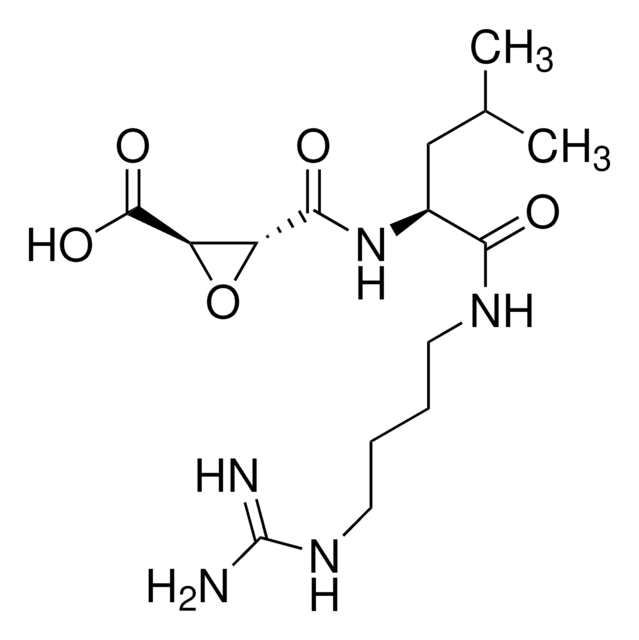
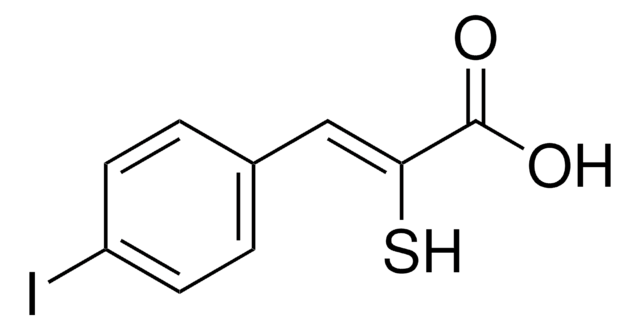
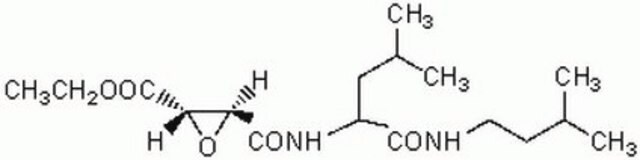
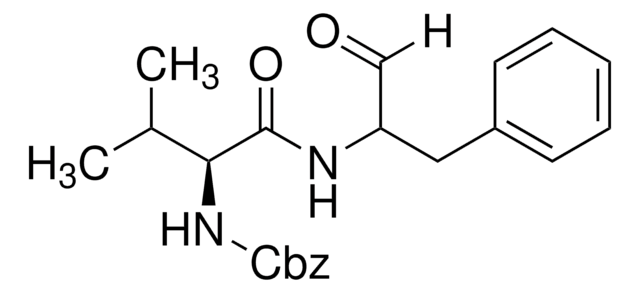
Contains 5 mg of ALLN (Cat. No. 208719), 25 mg of Calpain Inhibitor III (Cat. No. 208722), 5 mg of Calpeptin (Cat. No. 03-34-0051), 1 mg of EST (Cat. No. 330005), and 5 mg of PD 150606 (Cat. No. 513022).
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Cell permeable: yes
Primary Target
calpain 1, calpain 2
calpain 1, calpain 2
Reversible: no
Conditionnement
Packaged under inert gas
Avertissement
Toxicity: Multiple Toxicity Values, refer to MSDS (O)
Autres remarques
Johnson, G.V.W., and Guttmann, R.P. 1997. BioEssays19, 1011.
Kampfl, A., et al. 1997. J. Neurotauma14, 121.
Sorimachi, H., et al., 1997. Biochem. J.328, 721.
Bartus, R.T., et al. 1995. Neurol. Res.17, 249.
Wang, K.K.W., and Yuen, P-W. 1994. Trends Pharmacol. Sci.15, 412.
Saito, K., et al. 1993. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA90, 2628.
Goll, D.E., et al. 1992. BioEssays14, 549.
Kampfl, A., et al. 1997. J. Neurotauma14, 121.
Sorimachi, H., et al., 1997. Biochem. J.328, 721.
Bartus, R.T., et al. 1995. Neurol. Res.17, 249.
Wang, K.K.W., and Yuen, P-W. 1994. Trends Pharmacol. Sci.15, 412.
Saito, K., et al. 1993. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA90, 2628.
Goll, D.E., et al. 1992. BioEssays14, 549.
Informations légales
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique


![1,1′-[4,8-Bis[5-(2-ethylhexyl)-2-thienyl]benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]dithiophene-2,6-diyl]bis[1,1,1-trimethylstannane]](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/611/912/a638a6fe-ca7b-4674-8023-df4c0921a9fd/640/a638a6fe-ca7b-4674-8023-df4c0921a9fd.png)