1.01692
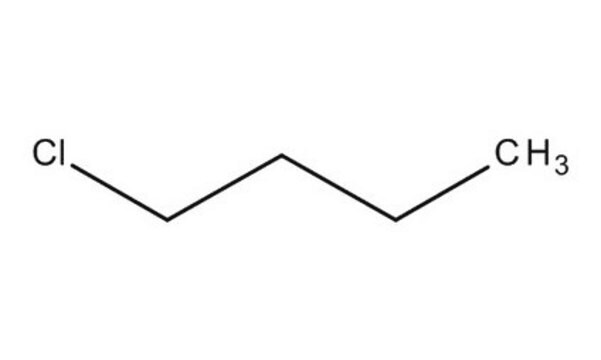
1-Chlorobutane
for liquid chromatography LiChrosolv®
Synonyme(s) :
1-Chlorobutane, n-Butyl chloride
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Pression de vapeur
110 hPa ( 20 °C)
Niveau de qualité
Gamme de produits
LiChrosolv®
Qualité
isocratic
Pureté
≥99.8% (GC)
Forme
liquid
Température d'inflammation spontanée
280 °C
Puissance
2200 mg/kg LD50, oral (Rat)
Limite d'explosivité
1.8-10.1 % (v/v)
Technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
Impuretés
≤0.0002 meq/g Acidity
≤0.0002 meq/g Alkalinity
≤0.01% Water
Résidus d'évap.
≤2.0 mg/L
Transmittance
227 nm, ≥60%
232 nm, ≥80%
250 nm, ≥98%
Point d'ébullition
79 °C/1013 hPa
Pf
-123 °C
Température de transition
flash point -17 °C
Densité
0.886 g/cm3 at 20 °C
Température de stockage
2-30°C
InChI
1S/C4H9Cl/c1-2-3-4-5/h2-4H2,1H3
Clé InChI
VFWCMGCRMGJXDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Description générale
Application
- Cl atoms-initiated degradation of 1-Chlorobutane and 2-Chlorobutane: This study investigates the kinetics and product analysis of the degradation of 1-Chlorobutane initiated by chlorine atoms. It provides insights into the atmospheric implications of halogenated hydrocarbons, relevant for environmental monitoring and analysis (Kar & Rajakumar, 2023).
- Efficient Remediation of p-chloroaniline Contaminated Soil: Utilizing activated persulfate in the presence of nanosized zero-valent iron/biochar composites, this study demonstrates a method that might be adaptable for the remediation of environments contaminated with similar compounds like 1-Chlorobutane. This is particularly valuable for environmental scientists and lab technicians working on soil decontamination (Guo et al., 2023).
- Rate Coefficient and Mechanism of the OH-Initiated Degradation of 1-Chlorobutane: Focusing on the atmospheric degradation of 1-Chlorobutane by hydroxyl radicals, this research provides critical data for understanding the environmental impact and the chemical behavior of 1-Chlorobutane in the atmosphere, important for researchers in environmental science and atmospheric chemistry (Jara-Toro et al., 2020).
- Genetic programming of catalytic Pseudomonas putida biofilms for boosting biodegradation of haloalkanes: This research demonstrates the genetic modification of bacteria to enhance their ability to degrade haloalkanes, including 1-Chlorobutane. This could interest principle investigators in biotech and pharma researching new methods of biodegradation for industrial applications (Benedetti et al., 2016).
Notes préparatoires
Remarque sur l'analyse
Identity (IR): conforms
Evaporation residue: ≤ 2.0 mg/l
Water: ≤ 0.01 %
Acidity: ≤ 0.0002 meq/g
Alkalinity: ≤ 0.0002 meq/g
Transmission (at 227 nm): ≥ 60 %
Transmission (at 232 nm): ≥ 80 %
Transmission (from 250 nm): ≥ 98 %
Filtered by 0.2 µm filter
Autres remarques
Informations légales
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Asp. Tox. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
10.4 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
-12 °C - closed cup
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique