716448
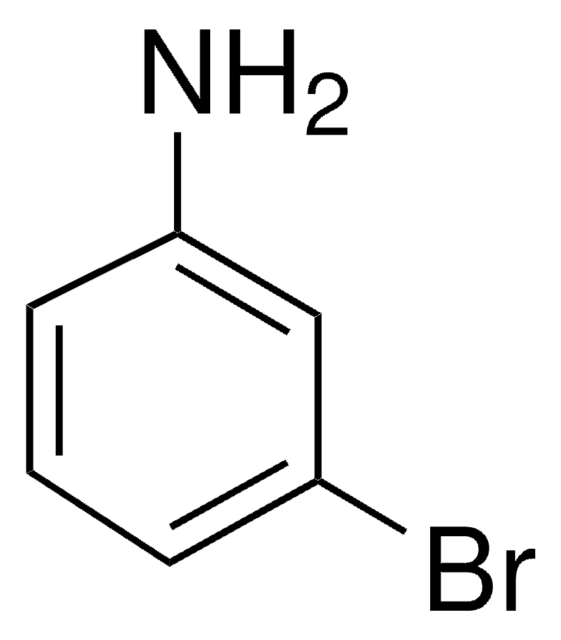
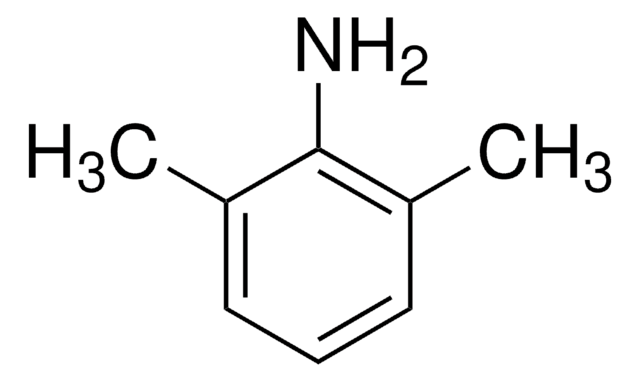
3-Aminobiphenyl
97%
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Formule empirique (notation de Hill):
C12H11N
Numéro CAS:
Poids moléculaire :
169.22
Numéro MDL:
Code UNSPSC :
12352100
ID de substance PubChem :
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.22
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
97%
Forme
solid
Pf
28-33 °C
Groupe fonctionnel
phenyl
Chaîne SMILES
Nc1cccc(c1)-c2ccccc2
InChI
1S/C12H11N/c13-12-8-4-7-11(9-12)10-5-2-1-3-6-10/h1-9H,13H2
Clé InChI
MUNOBADFTHUUFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organes cibles
Respiratory system
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
>230.0 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
> 110 °C - closed cup
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
M Maclure et al.
American journal of public health, 79(10), 1381-1384 (1989-10-01)
The hypothesis that involuntary exposure to tobacco smoke--passive smoking--results in greater risk of cancer was assessed by measuring the levels of two known carcinogens in the blood of 57 nonsmokers with varying degrees of involuntary exposure, including six heavily exposed
M S Bryant et al.
IARC scientific publications, (89)(89), 133-136 (1988-01-01)
In a population-based study in Turin, Italy, smokers of blond tobacco showed 4-aminobiphenyl (4-ABP) adduct levels some three times higher than nonsmoking subjects, and smokers of black tobacco showed levels about five times greater than nonsmokers. A dose-response relationship between
Paul L Skipper et al.
Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology, 12(6), 503-507 (2003-06-20)
Roughly one-half of bladder cancer incidence in the United States can be attributed to known causes, mainly cigarette smoking, and it has been hypothesized that the aromatic amines in tobacco smoke are important etiological agents. Nonsmokers are also exposed, through
J W Gorrod et al.
Anticancer research, 6(4), 729-731 (1986-07-01)
The metabolism of 3-aminobiphenyl (3-ABP) and 3-acetamidobiphenyl (3-AABP) has been studied using fortified rat liver microsomal preparations. Metabolites in concentrates of ether extracts from hepatic microsomal preparations were analysed by TLC and GLC. The metabolites were characterised by a comparison
G Ronco et al.
British journal of cancer, 61(4), 534-537 (1990-04-01)
In a previous study we found that aromatic amines, particularly 4-aminobiphenyl, formed haemoglobin adducts at higher concentrations in the blood of smokers compared to non-smokers. We re-analyse here data on haemoglobin adducts of 14 aromatic amines in order to ascertain
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique![[Pd(OAc)2]3 reagent grade, 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/508/249/99a0ef2c-b77c-4d73-8ed9-0cca05b6b41f/640/99a0ef2c-b77c-4d73-8ed9-0cca05b6b41f.png)