685070
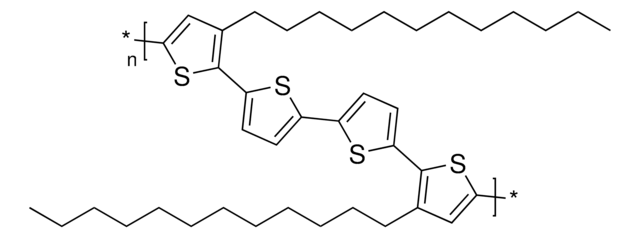
Poly[(9,9-dioctylfluorenyl-2,7-diyl)-co-bithiophene]
99.9%
Synonyme(s) :
F8T2, Poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene-alt-bithiophene), Poly[[2,2′-bithiophene]-5,5′-diyl(9,9-dioctyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)]
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
99.9%
Forme
powder
Poids mol.
average Mn >20,000
Fluorescence
λex 400 nm; λem 497 nm in chloroform (at Mn = 20,000)
Propriétés du semi-conducteur
P-type (mobility=5×10−3 cm2/V·s)
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Polymer is end-capped with 3,5-dimethylbenzene.
Application
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
The development of high-performance conjugated organic molecules and polymers has received widespread attention in industrial and academic research.
Organic photovoltaics (OPVs) represent a low-cost, lightweight, and scalable alternative to conventional solar cells. While significant progress has been made in the development of conventional bulk heterojunction cells, new approaches are required to achieve the performance and stability necessary to enable commercially successful OPVs.
There is widespread demand for thin, lightweight, and flexible electronic devices such as displays, sensors, actuators, and radio-frequency identification tags (RFIDs). Flexibility is necessary for scalability, portability, and mechanical robustness.
Global Trade Item Number
| Référence | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 685070-250MG | 4061832987194 |
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique![Poly[(9,9-di-n-octylfluorenyl-2,7-diyl)-alt-(benzo[2,1,3]thiadiazol-4,8-diyl)] average Mn ≤25000](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/428/661/1c4ebb98-9d51-48c0-96c7-e556ca425aa4/640/1c4ebb98-9d51-48c0-96c7-e556ca425aa4.png)