517003
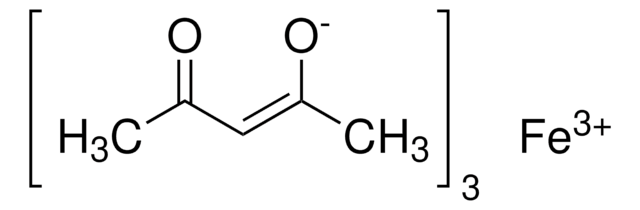
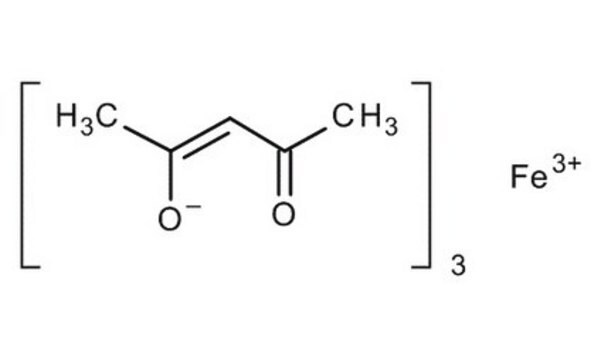
Iron(III) acetylacetonate
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
2,4-Pentanedione iron(III) derivative, Fe(acac)3, Ferric acetylacetonate, Iron(III) 2,4-pentanedionate
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Essai
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Forme
powder
Pertinence de la réaction
core: iron
reagent type: catalyst
Pf
180-182 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Densité
5.24 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Chaîne SMILES
CC(=O)\C=C(\C)O[Fe](O\C(C)=C/C(C)=O)O\C(C)=C/C(C)=O
InChI
1S/3C5H8O2.Fe/c3*1-4(6)3-5(2)7;/h3*3,6H,1-2H3;/q;;;+3/p-3/b3*4-3-;
Clé InChI
AQBLLJNPHDIAPN-LNTINUHCSA-K
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- A iron precursor for the synthesis of Fe3O4/carbon composite fibers via forcespinning technique. This composite material used in the formation of high-performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries.
- A precursor for the synthesis of iron-containing metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for the applications in rechargeable alkali-ion batteries.
- An additive to enhance the efficiency of the N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) catalyst in the oxidation of cumene.
- A solvent activation agent in the fabrication of polyamide membranes, which are used in reverse osmosis (RO) applications.
- As a MOCVD precursor for highly crystalline (Zn,Fe)Fe2O4 films and magnetic property measurements of these films. Iron (III) acetylacetonate may be used as a precursor for the synthesis of water-soluble magnetite nanoparticles, which may find applications in magnetic hyperthermia treatment.
- As a MOCVD precursor for highly crystalline (Zn,Fe)Fe2O4 films and magnetic property measurements of these films.
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Solvothermal synthesis is a method for preparing a variety of materials such as metals, semiconductors, ceramics, and polymers.
Professor Randal Lee (University of Houston, USA) discusses design considerations for iron oxide magnetic nanospheres and nanocubes used for biosensing, including synthetic procedures, size, and shape. The effects of these variables are discussed for various volumetric-based and surface-based detection schemes.
Professor Randal Lee (University of Houston, USA) discusses design considerations for iron oxide magnetic nanospheres and nanocubes used for biosensing, including synthetic procedures, size, and shape. The effects of these variables are discussed for various volumetric-based and surface-based detection schemes.
Magnetic nanoparticles have attracted tremendous attention due to their novel properties and their potential applications in magnetic recording, magnetic energy storage and biomedicine.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique