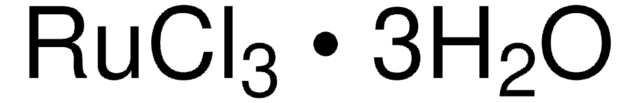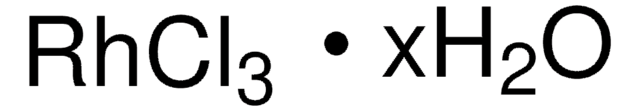208523
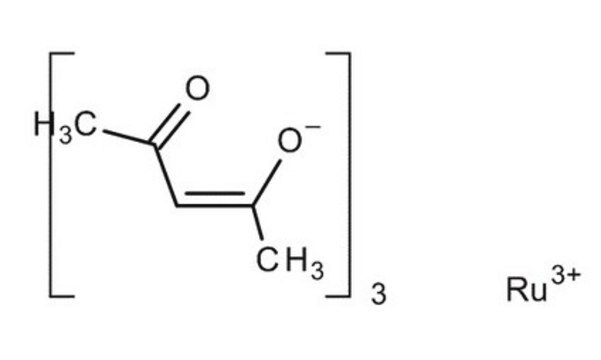
Ruthenium(III) chloride
Ru content 45-55%
Synonyme(s) :
Ruthenium trichloride
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Forme
solid
Pertinence de la réaction
core: ruthenium
reagent type: catalyst
reaction type: Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization (ATRP)
Densité
3.11 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Chaîne SMILES
Cl[Ru](Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/3ClH.Ru/h3*1H;/q;;;+3/p-3
Clé InChI
YBCAZPLXEGKKFM-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- In the synthesis of β‐amino alcohols by nucleophilic opening of epoxides with anilines.
- In the acetylation of varies of phenols, alcohols, thiols, and amines under mild conditions.
- In the synthesis of α‐aminonitriles by mixing aldehydes, amines, and trimethylsilyl cyanides.
Autres remarques
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Code de la classe de stockage
8B - Non-combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Tools for Performing ATRP
Applying ARGET ATRP to the Growth of Polymer Brush Thin Films by Surface-initiated Polymerization
We presents an article about Copper(I)-mediated Living Radical Polymerization in the Presence of Pyridylmethanimine Ligands, and the emergence of living radical polymerization mediated by transition metal catalysts in 1995, which was a seminal piece of work in the field of synthetic polymer chemistry.
Protocoles
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique