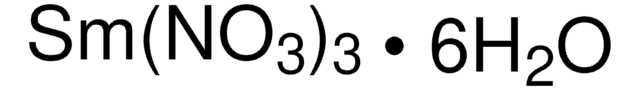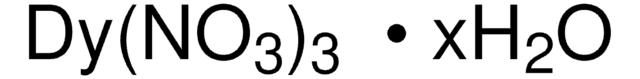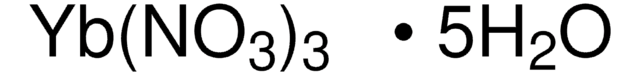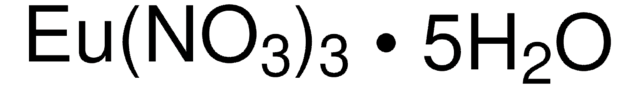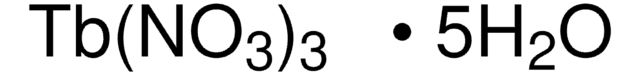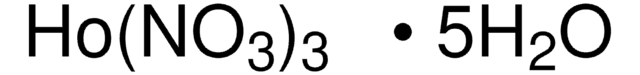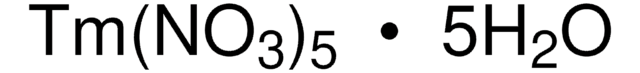205133
Praseodymium(III) nitrate hexahydrate
99.9% trace metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
Praseodymium trinitrate hexahydrate
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
99.9% trace metals basis
Forme
crystalline
Pertinence de la réaction
reagent type: catalyst
core: praseodymium
Impuretés
≤2000 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
Chaîne SMILES
O.O.O.O.O.O.[Pr+3].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/3NO3.6H2O.Pr/c3*2-1(3)4;;;;;;;/h;;;6*1H2;/q3*-1;;;;;;;+3
Clé InChI
LXXCECZPOWZKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- A dopant to fabricate dye-sensitized solar cells. The addition of rare earth enhances the power conversion efficiency of solar cells by narrowing the band gap of photoanode materials.
- A precursor to synthesize high entropy lanthanide oxysulfides ( wide band gap semiconductors).
- To synthesize functionalized UV-emitting nanocomposite for photodynamic cancer therapy.
- To fabricate Pr-doped MoO3 thinfilms for gas sensing applications.
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Ox. Sol. 3 - Skin Irrit. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
5.1B - Oxidizing hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Innovation in dental restorative materials is driven by the need for biocompatible and natural-appearing restoration alternatives. Conventional dental materials like amalgam and composite resins have inherent disadvantages.
The rare earth elements impact nearly everyone in the world. All of the people living in advanced technological countries and almost all those living in third world countries utilize the rare earths in their everyday living—the car that one drives (gasoline is refined from oil using rare earth catalysts and catalytic converters reduce the polluting emissions from the automotive exhaust), watching the news on TV (the red and green colors in TV screens), the telephones and computers we use to communicate (the permanent magnets in speakers and disc drives), just to name a few examples.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique