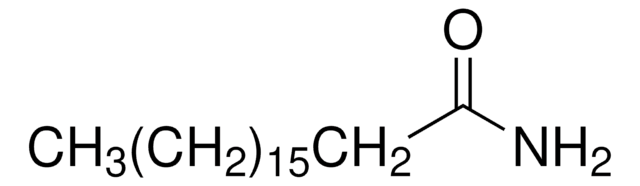S8439
Stearoyl ethanolamide
≥98%, crystalline
Synonym(s):
N-Stearoylethanolamine, NSE
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C20H41NO2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
327.55
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.83
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98%
form
crystalline
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NCCO
InChI
1S/C20H41NO2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-20(23)21-18-19-22/h22H,2-19H2,1H3,(H,21,23)
InChI key
OTGQIQQTPXJQRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
rat ... Cnr1(25248)
General description
Stearoyl ethanolamide, also called N-stearoylethanolamine (NSE) is present ubiquitously in all mammals. It exists in three isoforms when synthesized. It has therapeutic potential to modulate immune and inflammatory responses. It also possess antioxidative and membranoprotective functionality. NSE molecules pack in tail-to-tail fashion in lipid bilayer.
Application
Stearoyl ethanolamide (NSE) has been used as standard for quantifying in house synthesized NSE using thin layer chromatography.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Most abundant fatty acid ethanolamide produced by PLD hydrolysis of cell membrane phospholipids.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Murat Oz et al.
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 434(2), 344-351 (2005-01-11)
The effects of saturated long-chain (C: 16-22) N-acylethanolamines and a series of saturated fatty acids with the same length of carbon chains were investigated on depolarization-induced (45)Ca(2+) fluxes mediated by voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels in transverse tubule membrane vesicles from rabbit
Salvatore Terrazzino et al.
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 18(13), 1580-1582 (2004-08-04)
Given the recent demonstration that oleoylethanolamide (OEA), a cannabinoid receptor-inactive N-acylethanolamine, decreases food intake by activating the nuclear receptor PPARalpha (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha) in the periphery, we here evaluated the effects of both saturated and unsaturated C18 N-acylethanolamides (C18:0;
M Dalle Carbonare et al.
Journal of neuroendocrinology, 20 Suppl 1, 26-34 (2008-05-09)
N-acylethanolamines, which include the endocannabinoid anandamide and the cannabinoid receptor-inactive saturated compounds N-palmitoyl ethanolamine and N-stearoyl ethanolamine, are ethanolamines of long-chain fatty acids degraded by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) known to accumulate in degenerating tissues and cells. Whilst much
Mauro Maccarrone et al.
The Biochemical journal, 366(Pt 1), 137-144 (2002-05-16)
Stearoylethanolamide (SEA) is present in human, rat and mouse brain in amounts comparable with those of the endocannabinoid anandamide (arachidonoylethanolamide; AEA). Yet, the biological activity of SEA has never been investigated. We synthesized unlabelled and radiolabelled SEA to investigate its
Polymorphism of N-stearoylethanolamine: differential scanning calorimetric, vibrational spectroscopic (FTIR), and crystallographic studies
Wouters J, et al.
Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 119(1), 13-21 (2002)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service