N1665
5′-Nucleotidase human
recombinant, expressed in CHO cells, vial of 6-12 μg
Synonym(s):
CD73, NT5E, ecto-5′-nucleotidase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in CHO cells
Quality Level
description
contains a C-terminal 6-His tag
Assay
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
form
solution
enzyme activity
≥15 units/mg protein
mol wt
~61 kDa by SDS-PAGE (reducing)
packaging
vial of 6-12 μg
impurities
≤1.0 EU/μg endotoxin
NCBI accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... NT5E(4907)
General description
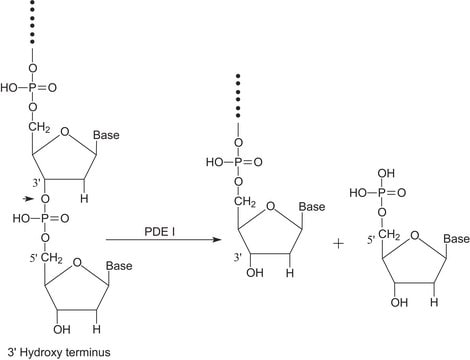
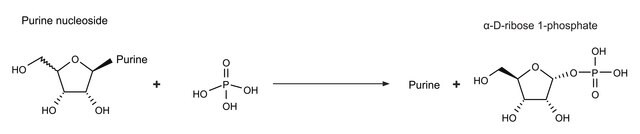
5′-Nucleotidase is an extracellular enzyme found in a wide variety of mammalian cells. It helps to accelerate the hydrolysis reaction of phosphate group from 5′ nucleotides, resulting in corresponding nucleosides.
Biochem/physiol Actions
5′-Nucleotidase has various clinical significances. It is a key molecule in the regulation of cancer cells proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro tumor angiogenesis, and tumor immune escape in vivo. Due to this important role, the enzyme is a potential target for cancer research. It is also involved in salvage of extracellular nucleotides and plays a key role in the control of tissue homeostasis.
5′-nucleotidase, also known as CD73, is an extracellular enzyme that converts nucleoside-5′−monophosphates to nucleosides with a substrate preference of AMP. Native 5′-nucleotidase is a GPI-anchored protein whose exporession is upregulated by hypoxia. 5′-nucleotidase has many functions in vivo including the generation of extracellular adenosine.
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of inorganic phosphorus from adenosine 5′-monophosphate per min at pH 9.0 at 37 °C.
Physical form
Supplied as a solution containing Tris, NaCl, CaCl2, and 20% glycerol.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
F W Sunderman
Annals of clinical and laboratory science, 20(2), 123-139 (1990-03-01)
This review delineates the subcellular distribution, biochemical characteristics, and metabolic functions of 5'-nucleotidase (5'NT), summarizes the analytical biochemistry of 5'NT, and assesses the clinical significance of 5'NT determinations in body fluids, cells, and tissues. Salient aspects of the clinical biochemistry
Zhao-wei Gao et al.
BioMed research international, 2014, 460654-460654 (2014-08-16)
Purinergic signaling has emerged as an important player in cancer progression and is regulated by a series of nucleotidases. Among the enzyme cascade, CD73, which catelyzes AMP breakdown to adenosine, has been found to be overexpressed in many types of
5'-Nucleotidase: molecular structure and functional aspects.
H Zimmermann
The Biochemical journal, 285 ( Pt 2), 345-365 (1992-07-15)
Isolation of a plasma-membrane subfraction from rat liver containing an insulin-sensitive cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase.
P D House et al.
European journal of biochemistry, 24(3), 429-437 (1972-01-21)
Anna Wilk et al.
Scientific reports, 10(1), 651-651 (2020-01-22)
Changes in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels that compromise mitochondrial function trigger release of DNA damaging reactive oxygen species. NAD+ levels also affect DNA repair capacity as NAD+ is a substrate for PARP-enzymes (mono/poly-ADP-ribosylation) and sirtuins (deacetylation). The ecto-5'-nucleotidase CD73
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service