L3012
Lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli O111:B4
purified by gel-filtration chromatography
Synonym(s):
LPS
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
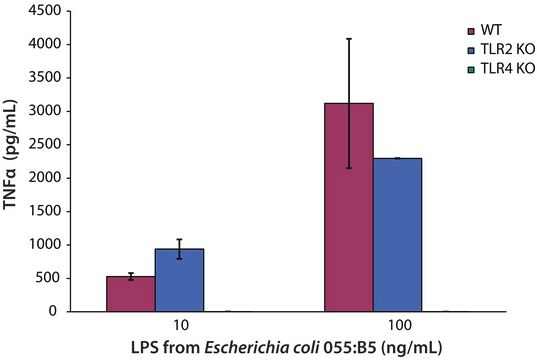
All Photos(4)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Escherichia coli (O111:B4)
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
purified by
gel-filtration chromatography
impurities
<1% Protein
color
white to faint yellow
solubility
water: soluble
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
This product is extracted from E. coli serotype O111:B4 and purified by gel filtration. The source strain is from a private collection. This LPS serotype has been used to stimulate B-cells and induce NOS in human hepatocytes.
Application
Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) are characteristic components of the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria. LPS and its lipid A moiety stimulate cells of the innate immune system by the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), a member of the Toll-like receptor protein family, which recognizes common pathogen-associated molecular-patterns (PAMPs).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are localized in the outer layer of the membrane and are, in noncapsulated strains, exposed on the cell surface. They contribute to the integrity of the outer membrane, and protect the cell against the action of bile salts and lipophilic antibiotics.
Preparation Note
The product is soluble in water (5 mg/ml) or cell culture medium (1 mg/ml) yielding a hazy, faint yellow solution. A more concentrated, though still hazy, solution (20 mg/ml) has been achieved in aqueous saline after vortexing and warming to 70-80 oC. Lipopolysaccharides are molecules that form micelles in every solvent. Hazy solutions are observed in water and phosphate buffered saline. Organic solvents do not give clearer solutions. Methanol yields a turbid suspension with floaters, while water yields a homogeneously hazy solution.
Other Notes
To gain a comprehensive understanding of our extensive range of Lipopolysaccharides for your research, we encourage you to visit our Carbohydrates Category page.
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Rong Huang et al.
Bone research, 5, 17019-17019 (2017-12-22)
The activation of M1 macrophages can be achieved by stimulating them with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ). However, M1 can be found under physiological conditions without any pathological stimuli. This study aimed to understand the involvement of RANKL-induced M1 macrophages
Matthew G Frank et al.
Brain, behavior, and immunity, 73, 352-363 (2018-05-29)
Exposure to stressors induces anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors, which are mediated, in part, by neuroinflammatory processes. Recent findings demonstrate that treatment with the immunoregulatory and anti-inflammatory bacterium, Mycobacterium vaccae (M. vaccae), attenuates stress-induced exaggeration of peripheral inflammation and stress-induced anxiety-like
Sheng Song et al.
Molecular neurobiology, 56(4), 2653-2669 (2018-07-28)
Environmental toxicant exposure has been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD). Clinical manifestations of non-motor and motor symptoms in PD stem from decades of progressive neurodegeneration selectively afflicting discrete neuronal populations along a caudo-rostral axis. However, recapitulating
Hui Wang et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 8519-8519 (2017-08-19)
Airway epithelial cell-derived thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and IL-33 can enhance lung-resident group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), and they play an important role in the development of allergic diseases. This study tests the hypothesis that Der f 31 (Dermatophagoides
Norihiko Takeda et al.
Genes & development, 24(5), 491-501 (2010-03-03)
Hypoxic response and inflammation both involve the action of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha. Previous studies have revealed that both HIF-alpha proteins are in a number of aspects similarly regulated post-translationally. However, the functional interrelationship of these two
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service