D5540
Diaphorase from Clostridium kluyveri
lyophilized powder, 3.0-20.0 units/mg protein (biuret)
Synonym(s):
Diaphorase, Lipoamide Dehydrogenase, Lipoyl Dehydrogenase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bacterial (Clostridium kluyveri)
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
3.0-20.0 units/mg protein (biuret)
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Diaphorase from Clostridium kluyveri, or Lipoyl dehydrogenase, has been used in a study to assess the protein-protein interactions in assembly of lipoic acid on the 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases of aerobic metabolism. Lipoyl dehydrogenase has also been used in a study to investigate the redox regulation of tyrosine nitration and 3-nitrotyrosine reduction by antioxidants.
Methylene blue (MB)-containing polyacrylamide nanoparticle platforms (NPs) were tested in solution with diaphorase from Clostridium kluyveri and the cofactor NADH. this test done done to check whether the encapsulation of MB in NPs could prevent the reduction of MB, and thus protect its photodynamic effectiveness. The enzyme from Sigma has been used along with aldehyde dehydrogenase to construct a biosensor for acetaldehyde by immobilization. It has also been used in the reoxidation of NADP to NADPH. This reaction simultaneously catalyzed the conversion of resazurin into the highly fluorescent resorufin, and also allowed the detection of minute amounts of NAADP. NAADP was initially converted to NADP and NADPH by other enzymes.
Packaging
Sold on the basis of native diaphorase units.
Other Notes
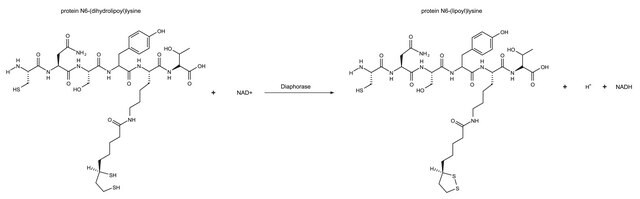
The name "Diaphorase" has been loosely applied to several enzymes which catalyze the oxidation of either β-NADH or β-NADPH in the presence of an electron acceptor such as methylene blue or 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol. Many different assay procedures and "units" are used.
Diaphorases which are specific for either β-NADH or β-NADPH are known. The pig heart enzyme of Straub seems to have native diaphorase (β-NADH specific) as well as lipoic and lipoamide dehydrogenase activities. It is reported to be a single protein. However, Massey reports that "diaphorase" is probably a denatured lipoamide dehydrogenase. Pre-incubation of the pig heart preparation with Cu2+ reduces the lipoamide dehydrogenase activity and proportionately increases the β-NADH diaphorase activity. In our laboratory, we have demonstrated this copper effect to some degree on the pig heart enzyme, but no appreciable effect was observed on the Clostridium kluyveri or torula yeast preparations. The lipoamide dehydrogenase:diaphorase ratio is a measure of the denaturation.
Diaphorases which are specific for either β-NADH or β-NADPH are known. The pig heart enzyme of Straub seems to have native diaphorase (β-NADH specific) as well as lipoic and lipoamide dehydrogenase activities. It is reported to be a single protein. However, Massey reports that "diaphorase" is probably a denatured lipoamide dehydrogenase. Pre-incubation of the pig heart preparation with Cu2+ reduces the lipoamide dehydrogenase activity and proportionately increases the β-NADH diaphorase activity. In our laboratory, we have demonstrated this copper effect to some degree on the pig heart enzyme, but no appreciable effect was observed on the Clostridium kluyveri or torula yeast preparations. The lipoamide dehydrogenase:diaphorase ratio is a measure of the denaturation.
Unit Definition
One unit of either "diaphorase" or "lipoyl" dehydrogenase will oxidize 1.0 μmole of β-NADH per min at pH 7.5 at 25 °C, with the corresponding reduction of 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol
inhibitor
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Wei Tang et al.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 369(2), 579-583 (2008-02-27)
The ability to prevent methylene blue (MB), a photosensitizer, from being reduced by plasma reductases will greatly improve its efficacy in photodynamic therapy (PDT) applications. We have developed a delivery approach for PDT by encapsulating MB using nanoparticle platforms (NPs).
Bachar H Hassan et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 286(10), 8263-8276 (2011-01-07)
Lipoic acid is a covalently attached cofactor essential for the activity of 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases and the glycine cleavage system. In the absence of lipoic acid modification, the dehydrogenases are inactive, and aerobic metabolism is blocked. In Escherichia coli, two pathways
Andreas Gasser et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 281(25), 16906-16913 (2006-04-22)
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) is the most potent activator of Ca2+ release from intracellular stores known today. Although recent reports have suggested an important function of NAADP in human T lymphocytes, direct evidence for receptor-induced formation of NAADP
Hauh-Jyun Candy Chen et al.
Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology, 9(2), 312-323 (2007-12-29)
Covalent modifications of proteins by endogenous reactive nitrogen oxide species lead to cytotoxic effects that are implicated in diseases associated with chronic infections and inflammation. Tyrosine nitration is a major post-translational modification of proteins by reactive nitrogen oxide species. Recent
Kirti Rani et al.
Indian journal of biochemistry & biophysics, 43(2), 98-104 (2006-09-08)
3alpha-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3alpha-HSD) from Pseudomonas testosteronei and diaphorase (lipoyl dehydrogenase) from Clostridium spp were immobilized individually onto alkylamine glass beads through glutaraldehyde coupling. A cost-effective enzymic colorimetric method for determination of bile acid in the serum and bile was developed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service