BCK488-IV-IM-S
In Vivo EdU Click Kit 488
sufficient for 100 assays
Synonym(s):
EdU Cell Proliferation Kit
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12161503
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
fluorescence
λex 496 nm; λem 516 nm
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
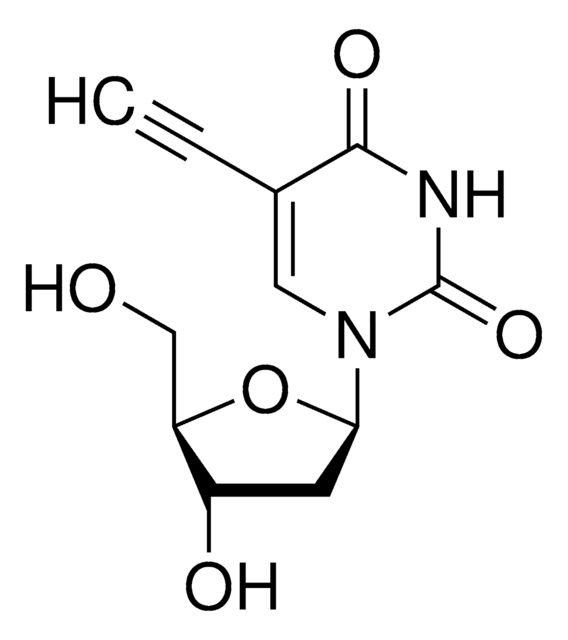
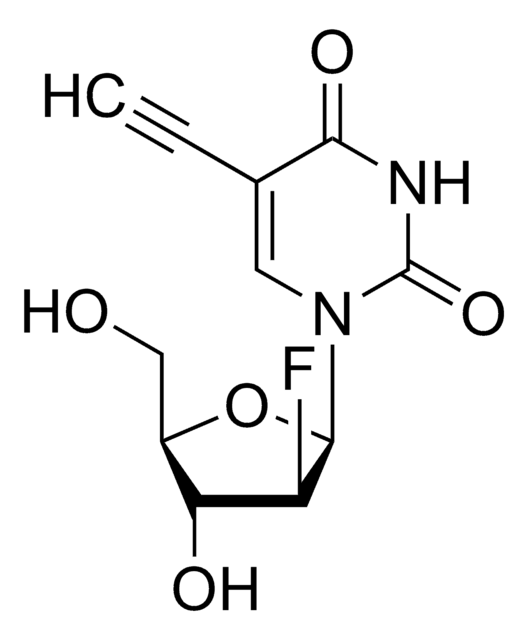
The Baseclick EdU In Vivo Kits provide a superior alternative to BrdU and [3H]thymidine assays for detection of cell proliferation in whole animals, showing no toxic effects. EdU (5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine) is a nucleoside analog to thymidine and is incorporated into DNA during active DNA synthesis. In contrast to BrdU assays, the EdU In Vivo Assays are not antibody based and therefore do not require DNA denaturation for detection of the incorporated nucleoside. Instead, the EdU In Vivo Kits utilize click chemistry for detection in a variety of dye fluorescent readouts. Furthermore, the streamlined detection protocol reduces both the total number of steps and significantly decreases the total amount of time. The simple click chemistry detection procedure is complete within 30 minutes and is compatible with multiplexing for content and context-rich results.The in vivo kits are designed in a sense that you combine one of the three baseclick EdU cell proliferation kits such as:
1. Imaging kit (BCK-IV-IM)
2. Flow cytometry kit (BCK-IV-FC)
3. High throughput screening – HTS kit (BCK-IV-HTS)
You can select the above kits with the dye of choice and the right EdU content for your animal model.
Depending on your animal model or the number of animals to be tested you can choose between three kit sizes S, M, and L with increasing EdU content, as indicated in the following table.
Kit Size Content of EdU
S 50 mg
M 500 mg
L 1000 mg
1. Imaging kit (BCK-IV-IM)
2. Flow cytometry kit (BCK-IV-FC)
3. High throughput screening – HTS kit (BCK-IV-HTS)
You can select the above kits with the dye of choice and the right EdU content for your animal model.
Depending on your animal model or the number of animals to be tested you can choose between three kit sizes S, M, and L with increasing EdU content, as indicated in the following table.
Kit Size Content of EdU
S 50 mg
M 500 mg
L 1000 mg
Application
in Vivo, Imaging
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Muta. 1B - Repr. 2
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Junhui Zhang et al.
Frontiers in pharmacology, 10, 368-368 (2019-05-02)
Endothelial cells play a critical role in the process of angiogenesis during skin wound healing. The migration and proliferation of endothelial cells are processes that are initiated by the hypoxic microenvironment in a wound, but the underlying mechanisms remain largely
Junhui Zhang et al.
International journal of biological sciences, 15(9), 1962-1976 (2019-09-17)
Both cell migration and proliferation are indispensable parts of reepithelialization during skin wound healing, which is a complex process for which the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. Here, we identify a novel role for microtubule-associated protein 4 (MAP4), a
Lingfei Li et al.
Cell communication and signaling : CCS, 20(1), 115-115 (2022-07-29)
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) involves various structural and functional changes because of chronic glycemic assault and kidney failure. Proteinuria is an early clinical manifestation of DN, but the associated pathogenesis remains elusive. This study aimed to investigate the role of microtubule
Yongmao Yu et al.
Journal of immunological methods, 350(1-2), 29-35 (2009-08-04)
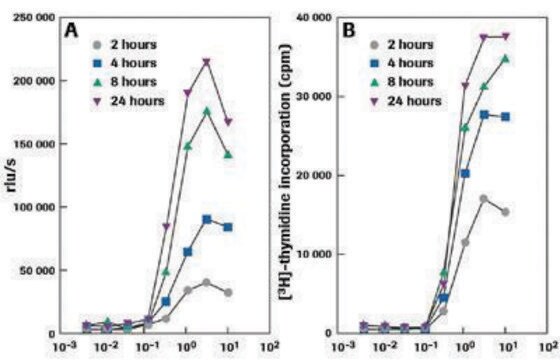
T lymphocyte proliferations can be measured by [(3)H]thymidine incorporation. However, many labs avoid this technique because of the need to use radioactive substrates. In addition, [(3)H]thymidine incorporation method does not permit simultaneous characterization of the proliferating cells. We developed the
Fatemah Chehrehasa et al.
Journal of neuroscience methods, 177(1), 122-130 (2008-11-11)
Labelling and identifying proliferating cells is central to understanding neurogenesis and neural lineages in vivo and in vitro. We present here a novel thymidine analogue, ethynyl deoxyuridine (EdU) for labelling dividing cells, detected with a fluorescent azide which forms a
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service