All Photos(1)
About This Item
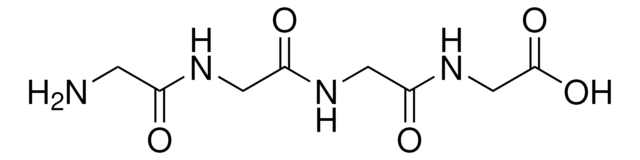
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C14H26N4O5
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
330.38
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
Product Name
Acetyl-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala, ≥95% (HPLC)
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
form
powder
solubility
water: 10 mg/mL, clear, colorless
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
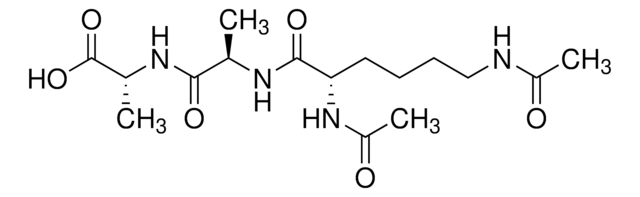
CC(NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(C)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C14H26N4O5/c1-8(12(20)17-9(2)14(22)23)16-13(21)11(18-10(3)19)6-4-5-7-15/h8-9,11H,4-7,15H2,1-3H3,(H,16,21)(H,17,20)(H,18,19)(H,22,23)
InChI key
GMSXMADYKTYBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Substrates
Substrate for carboxypeptidase G and DD from Streptomyces albus.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
D H Williams et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 280(5364), 711-714 (1998-05-23)
The cooperativity between binding of cell wall precursor analogs (ligands) to and antibiotic dimerization of the clinically important vancomycin group antibiotics was investigated by nuclear magnetic resonance. When dimerization was weak in the absence of a ligand, the increase in
L Varetto et al.
European journal of biochemistry, 162(3), 525-531 (1987-02-02)
Titration of the active-site serine DD-peptidase of Streptomyces R61 shows that formation of acyl enzyme during hydrolysis of the substrate Ac2-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala and enzyme inactivation by the beta-lactam compounds benzylpenicillin, N-acetylampicillin and ampicillin relies on the acidic form of an enzyme's
The structure of an asymmetric dimer relevant to the mode of action of the glycopeptide antibiotics.
P Groves et al.
Structure (London, England : 1993), 2(8), 747-754 (1994-08-15)
Glycopeptide antibiotics of the vancomycin group are of crucial clinical importance in the treatment of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)--the often lethal 'super-bug'--characterized by its resistance to a wide range of antibiotics in common use. The antibiotics exert their physiological
Eric C DiBiasio et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 202(20) (2020-08-12)
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) is the leading cause of human urinary tract infections (UTIs), and many patients experience recurrent infection after successful antibiotic treatment. The source of recurrent infections may be persistent bacterial reservoirs in vivo that are in a
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service