11534378910
Roche
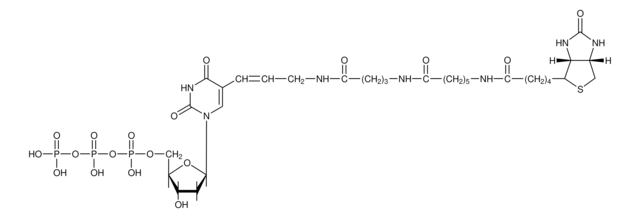
Tetramethyl-Rhodamine-5-dUTP
Synonym(s):
Rhodamine-5-dUTP tetralithium salt, Tetramethylrhodamine-5(6)-(5-[3-carboxamidoallyl]-2′-deoxyuridine 5′-triphosphate)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C37H40N5O18P3
Molecular Weight:
935.66
UNSPSC Code:
41116100
Recommended Products
grade
Molecular Biology
Quality Level
Assay
97.7% (HPLC)
form
solution
mol wt
990.5
packaging
pkg of 25 μL (25 nmol; 1mM)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
concentration
1.0 mmol/L (Tetramethylrhodamine-5-dUTP (Abs. 551 nm))
color
clear red
mp
~0 °C
solubility
water: miscible
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Tetramethylrhodamine is bound to deoxyuridine triphosphate via an amide linkage.
Application
Tetramethyl-Rhodamine-5-dUTP has been used in the labelling of DNA fragments and in the synthesis of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) probes.
Quality
Typical analysis: At least 85% Tetramethyl-Rhodamine-5-dUTP (HPLC, area%).
Analysis Note
Absorption: Absorption spectra available in the files.
Other Notes
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. For some in situ experiments, it is useful to label DNA with two fluorescent "tags," tetramethylrhodamine (red) and fluorescein (yellow).
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
does not flash
Flash Point(C)
does not flash
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Developmental stage influences chromosome segregation patterns and arrangement in the extremely polyploid, giant bacterium Epulopiscium sp. type B
Hutchison E, et al.
Molecular Microbiology, 107(1), 68-80 (2018)
Robert Hasterok et al.
Genetics, 173(1), 349-362 (2006-02-21)
As part of an initiative to develop Brachypodium distachyon as a genomic "bridge" species between rice and the temperate cereals and grasses, a BAC library has been constructed for the two diploid (2n = 2x = 10) genotypes, ABR1 and
rDNA cytogenetics and some structural variability in an Avena barbata Pott ex Link? A. sativa subsp. nuda (L.) Gillet et Magne amphiploid after 5-azaC treatment.
Florek M and Kosina R
Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 64(7), 1723-1741 (2017)
Insight into the karyotype evolution of brachypodium species using comparative chromosome barcoding.
Dominika Idziak et al.
PloS one, 9(3), e93503-e93503 (2014-03-29)
Paleogenomic studies based on bioinformatic analyses of DNA sequences have enabled unprecedented insight into the evolution of grass genomes. They have revealed that nested chromosome fusions played an important role in the divergence of modern grasses. Nowadays, studies on karyotype
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 11534378910 | 4061838703231 |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service