MABE1885
Anti-Histone H1 Antibody, clone 1G6
clone 1G6, from mouse
Synonym(s):
H1
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
NACRES:
NA.43
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
1G6, monoclonal
species reactivity
Drosophila
packaging
antibody small pack of 25 μg
technique(s)
ChIP: suitable (ChIP-seq)
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG1κ
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
Histone H1 (UniProt: P02255; also known as H1) is encoded by the His 1 gene (Gene ID: 318854) in Drosophila species. Histone H1 is a linker histone that is involved in the organization and maintenance of chromatin higher order structure and plays an active role in the control of DNA replication and cell proliferation. The linker histone H1 family members are a key component of chromatin and bind to the nucleosomal core particle around the DNA entry and exit sites. Histone H1 is essential for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structures. In metazoans, H1 histones are smaller in size with about 200 amino acids. They have a short N-terminal tail, a central globular domain, and a long basic C-terminal tail. The central globular domain is shown to be highly conserved among all H1 subtypes. Manipulating levels of H1 histone can lead to both up- and down-regulation of specific genes. Depletion of H1 results in a massively altered chromosome structure with loss of chromosome banding. In Drosophila, a 20% reduction in H1 content leads to cessation of growth beyond the larval stage. Histone H1 undergoes phosphorylation mainly in the tail region, especially the C-terminal tail, where several {(S/T)-P-X-(K/R)} motifs are located that are recognized by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Phosphorylation levels are reported to be lowest during the G1 phase of the cell cycle and increase during S phase and reach maximum levels in mitosis. (Ref.: Hergeth, SP., and Schneider, R (2015). EMBO Rep. 16(11); 1439-1453).
Specificity
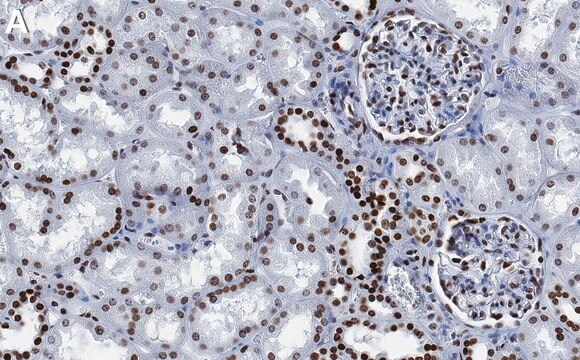
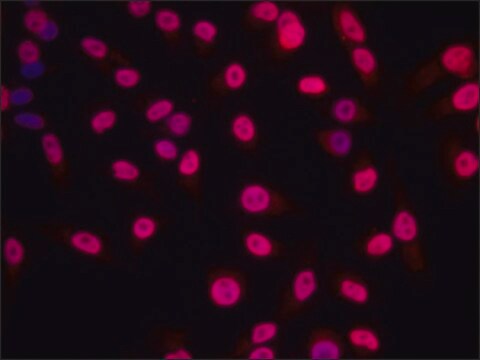
Clone 1G6 is a mouse monoclonal antibody that detects Histone H1 in Drosophila species.
Immunogen
GST-tagged recombinant fragment corresponding to 148 amino acids from the C-terminal half of Drosophila Histone H1.
Application
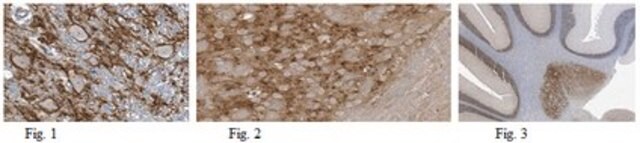
Anti-Histone H1, clone 1G6 Antibody, Cat. No. MABE1885, is a highly specific mouse monoclonal antibody that targets Drosophila Histone H1 and has been tested for use in Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP), ChIP-seq, Immunoprecipitation, and Western Blotting.
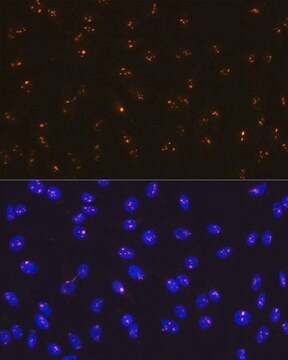
ChIP-seq Analysis: A representative lot detected Histone H1 in ChIP-seq applications (Iwasaki, Y.W., et. al. (2016). Mol Cell. 63(3):408-19).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated Histone H1 in Immunoprecipitation applications (Iwasaki, Y.W., et. al. (2016). Mol Cell. 63(3):408-19).
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Analysis (ChIP): A representative lot immunoprecipitated Histone H1 in Chromatin Immunoprecipitation applications (Iwasaki, Y.W., et. al. (2016). Mol Cell. 63(3):408-19).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated Histone H1 in Immunoprecipitation applications (Iwasaki, Y.W., et. al. (2016). Mol Cell. 63(3):408-19).
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Analysis (ChIP): A representative lot immunoprecipitated Histone H1 in Chromatin Immunoprecipitation applications (Iwasaki, Y.W., et. al. (2016). Mol Cell. 63(3):408-19).
Quality
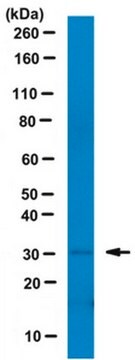
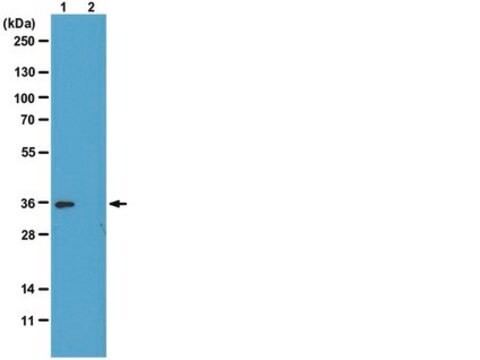
Evaluated by Western Blotting in Drosophila S2 cell lysate.
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:500 dilution of this antibody detected Histone H1 in Drosophila S2 cell lysate.
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:500 dilution of this antibody detected Histone H1 in Drosophila S2 cell lysate.
Target description
~35 kDa observed; 26.36 kDa calculated. Uncharacterized bands may be observed in some lysate(s).
Physical form
Format: Purified
Other Notes
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service