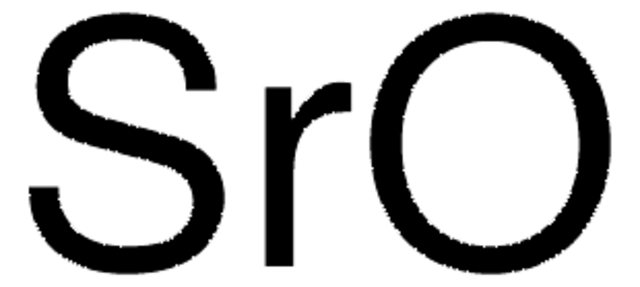460346
Strontium
dendritic pieces, purified by distillation, 99.9% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Strontium element
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
Sr
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
87.62
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12141504
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99.9% trace metals basis
form
dendritic pieces
purified by
distillation
reaction suitability
reagent type: reductant
resistivity
23 μΩ-cm, 20°C
bp
1384 °C (lit.)
mp
757 °C (lit.)
density
2.6 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
[Sr]
InChI
1S/Sr
InChI key
CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Dendritic strontium is a form of strontium metal that has a unique, tree-like or branching morphology. It is often made by electrodeposition. Dendritic strontium is a silvery-white metal that is highly reactive with water and oxygen, and it readily tarnishes in air. It has several important physical properties, including a melting point of 769 °C and a density of 2.54 g/cm3.
Application
Dendritic strontium has a number of important uses including use as a component of alloys, as a material for pyrotechnic devices, as a reagent in the production of ferrite magnets, and as a dopant in the production of semiconductors.
Dendritic-strontium can be applied in the solid state synthesis of a Zintl phase, SrSn3Sb4, with an anionic channel framework of 30-membered rings.It can also be used to make strontium-potassium-niobate (Sr2KNb5O15, SKN) which is of great interest for pyroelectric sensors and various electro-optic devices.
Used to make Strontium-potassium-niobate (Sr2KNb5O15, SKN). SKN is of great interest for pyroelectric sensors and various electro-optic devices.2
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Irrit. 2 - Water-react 1
Supplementary Hazards
Storage Class Code
4.3 - Hazardous materials which set free flammable gases upon contact with water
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Synthesis of Sr 2 KNb 5 O 15 Thin Films by Chemical Solution Deposition Method.
Sakamoto W, et al.
Journal of Materials Research, 14(04), 1495-1502 (1999)
Emily Y Tsui et al.
Nature chemistry, 5(4), 293-299 (2013-03-21)
Redox-inactive metals are found in biological and heterogeneous water oxidation catalysts, but, at present, their roles in catalysis are not well understood. Here, we report a series of high-oxidation-state tetranuclear-dioxido clusters comprising three manganese centres and a redox-inactive metal (M).
A Schaafsma et al.
Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 41(4), 225-249 (2001-06-13)
For early prevention or inhibition of postmenopausal and age-related bone loss, nutritional interventions might be a first choice. For some vitamins and minerals an important role in bone metabolism is known or suggested. Calcium and vitamin D support bone mineral
P J Marie et al.
Calcified tissue international, 69(3), 121-129 (2001-10-31)
The processes of bone resorption and formation are tightly governed by a variety of systemic and local regulatory agents. In addition, minerals and trace elements affect bone formation and resorption through direct or indirect effects on bone cells or bone
Martine Cohen-Solal
Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association, 17 Suppl 2, 30-34 (2002-03-21)
Although the prevalence of aluminium-related bone diseases has declined, osteomalacia still persists at a low prevalence. The redistribution of bone disease prevalence corresponds to evolving regimens in the treatment of renal disease. Studies have demonstrated an association between the accumulation
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service