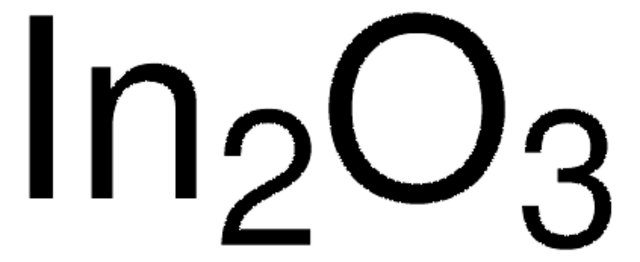289418
Indium(III) oxide
99.99% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Diindium trioxide, Indium sesquioxide
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
<0.01 mmHg ( 25 °C)
Quality Level
Assay
99.99% trace metals basis
form
powder
reaction suitability
reagent type: catalyst
core: indium
density
7.18 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
application(s)
battery manufacturing
SMILES string
O=[In]O[In]=O
InChI
1S/2In.3O
InChI key
SHTGRZNPWBITMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Comparative analysis on application conditions of indium (III) oxide-reinforced glasses in nuclear waste management and source transportation: A Monte Carlo study: This research explores the use of indium (III) oxide-reinforced glass for radioactive waste containment, highlighting its effectiveness and potential in nuclear waste management (ALMisned et al., 2023).
- Double-shelled hollow rods assembled from nitrogen/sulfur-codoped carbon coated indium oxide nanoparticles as excellent photocatalysts: Discusses the synthesis and application of indium oxide nanoparticles in photocatalysis, demonstrating significant enhancements in environmental cleanup technologies (Sun et al., 2019).
- Black indium oxide a photothermal CO2 hydrogenation catalyst: Investigates black indium oxide for its use in photocatalytic CO2 reduction, a critical process for sustainable energy and chemical synthesis (Wang et al., 2020).
- Material proposal for 2D indium oxide: This study proposes two-dimensional indium oxide, discussing its material characteristics and potential applications in electronics and optoelectronics (Kakanakova-Georgieva et al., 2021).
- Purification of indium by solvent extraction with undiluted ionic liquids: Examines the processes of extracting and purifying indium using green chemistry approaches, contributing to more sustainable practices in materials processing (Deferm et al., 2016).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Spectral conversion for solar cells is an emerging concept in the field of photovoltaics, and it has the potential to increase significantly the efficiency of solar cells. Lanthanide ions are ideal candidates for spectral conversion, due to their high luminescence efficiencies and rich energy level structure that allows for great flexibility in the upconversion and downconversion of photons in a wide spectral region (NIR-VIS-UV).
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service