158496
Proton-sponge®
99%
Synonym(s):
1,8-Bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene, N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethyl-1,8-naphthalenediamine
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
form
solid
mp
49-51 °C (lit.)
solubility
chloroform: soluble 50 mg/mL, clear (faint yellow to dark yellow to dark red)
functional group
amine
SMILES string
CN(C)c1cccc2cccc(N(C)C)c12
InChI
1S/C14H18N2/c1-15(2)12-9-5-7-11-8-6-10-13(14(11)12)16(3)4/h5-10H,1-4H3
InChI key
GJFNRSDCSTVPCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Proton-sponge is also referred to as 1,8-dimethylamino naphthalene. It is very strong base with weak nucleophilic character due to steric effects. It also participates in the reactions between arachno-6,9-C2B8H14 and selected acyl chlorides. It has been tested as an effective H+ scavenger.
Application
Legal Information
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
113 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service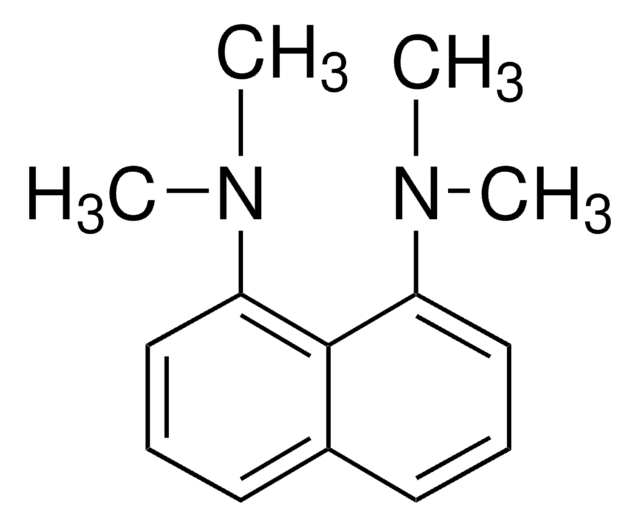




![1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/120/564/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb/640/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb.png)
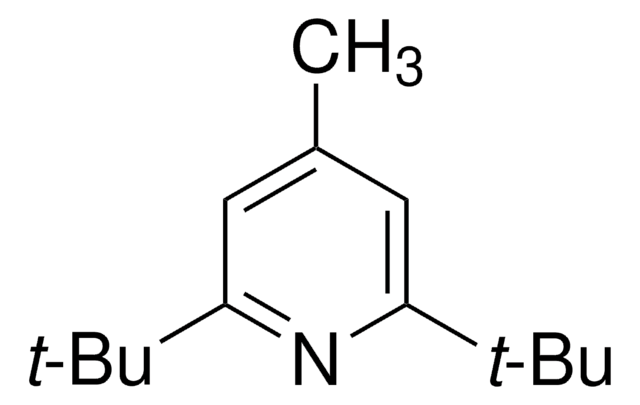

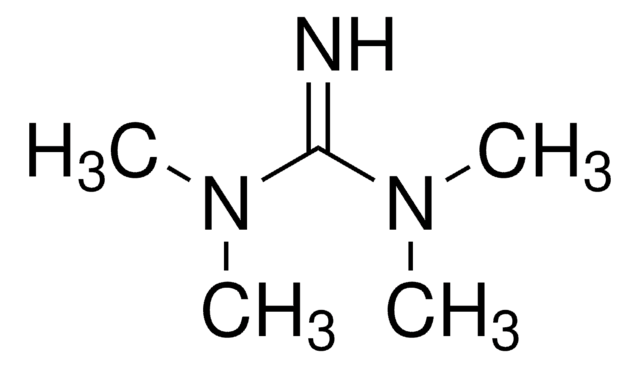
![7-Methyl-1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/237/769/028967ef-ca63-4f22-acc9-68f135a43b9a/640/028967ef-ca63-4f22-acc9-68f135a43b9a.png)
![2,8,9-Triisopropyl-2,5,8,9-tetraaza-1-phosphabicyclo[3,3,3]undecane](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/387/021/edaffe12-6e4b-4305-9030-749551ac828a/640/edaffe12-6e4b-4305-9030-749551ac828a.png)
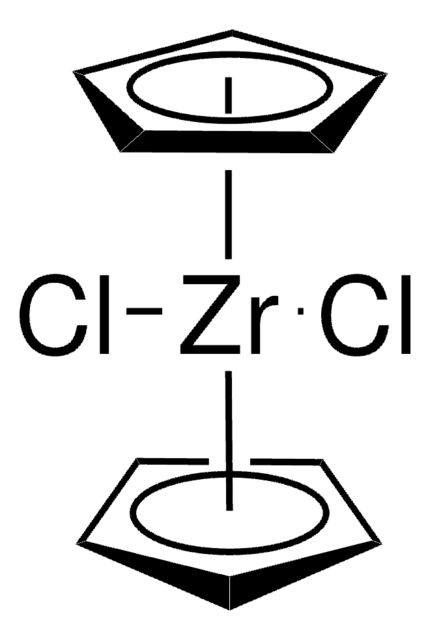


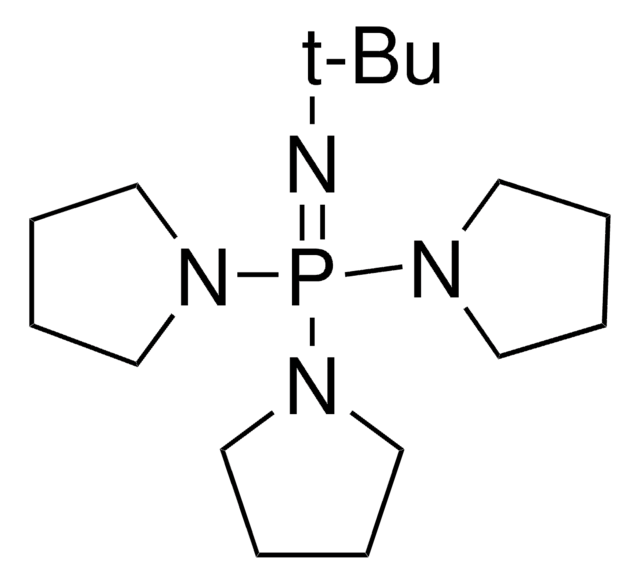
![1,5,7-Triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/171/446/333d560c-cff6-4958-b489-5acfb3057cce/640/333d560c-cff6-4958-b489-5acfb3057cce.png)