137030
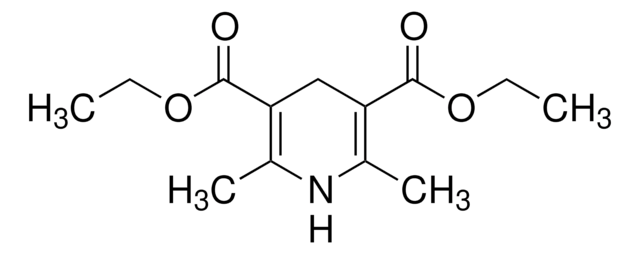
Diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,4,6-trimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
99%
Synonym(s):
3,5-Dicarbethoxy-1,4-dihydrocollidine, DDC
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C14H21NO4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
267.32
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
form
powder
mp
130-132 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C1C)C(=O)OCC
InChI
1S/C14H21NO4/c1-6-18-13(16)11-8(3)12(14(17)19-7-2)10(5)15-9(11)4/h8,15H,6-7H2,1-5H3
InChI key
CDVAIHNNWWJFJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
Diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,4,6-trimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate was used to induce Mallory-Denk body formation in mice in vivo.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,4,6-trimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate blocks the heme synthesis and prevents the induction of hepatic heme oxygenase-1 in mice.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Volker Mostert et al.
Drug metabolism reviews, 39(2-3), 619-626 (2007-09-06)
Heme oxygenase (HO)-1 is induced by oxidative stress and protects against oxidant injury. We examined the effect of rapid induction of hepatic HO-1 on serum iron level. Serum iron was approximately doubled within 6 h when HO-1 was induced by
Pavel Strnad et al.
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.), 48(3), 931-942 (2008-08-13)
The cytoplasmic hepatocyte inclusions, Mallory-Denk bodies (MDBs), are characteristic of several liver disorders, including alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. In mice, MDBs can be induced by long-term feeding with 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine (DDC) for 3 to 4 months or rapidly reformed in DDC-induced
Johanna R Schaub et al.
Nature, 557(7704), 247-251 (2018-05-04)
Transdifferentiation is a complete and stable change in cell identity that serves as an alternative to stem-cell-mediated organ regeneration. In adult mammals, findings of transdifferentiation have been limited to the replenishment of cells lost from preexisting structures, in the presence
Leila Jemail et al.
Scientific reports, 8(1), 6415-6415 (2018-04-25)
Kupffer cells (KCs) are key players in maintaining tissue homeostasis and are involved in various liver diseases. However, the roles of KCs in the pathogenesis of cholangiopathy are largely unknown. We aimed to investigate the precise roles of KCs in
Tohru Itoh et al.
FEBS letters, 583(4), 777-781 (2009-01-29)
In injured livers where hepatocyte growth is severely limited, facultative hepatic stem/progenitor cells, termed oval cells in rodents, are known to emerge and contribute to the regeneration process. Here, we investigated a possible involvement of Wnt signaling during mouse oval
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service