P2165
Protein A–Biotin from Staphylococcus aureus
lyophilized powder
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
conjugate
biotin conjugate
Quality Level
200
300
form
lyophilized powder
composition
Protein, ≥70% biuret
extent of labeling
3.0-8.0 mol biotin per mol Protein A
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
Protein A (SpA) is a 42kDa virulence factor produced by Staphylococcus aureus, and is composed of five highly homologous consecutive extracellular Ig-binding domains, namely domains E, D, A, B, and C. This protein is present in both secreted and membrane-associated forms.
Specificity
Binds IgG only from most mammals, except rat, goat, and sheep
Biochem/physiol Actions
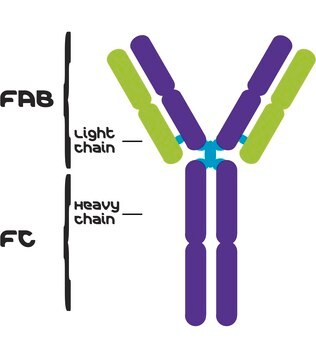
Protein A (SpA) causes B cells death in vitro, by binding to the Fc region of antibody and the Fab regions of the B-cell receptor, thus inhibiting its opsonophagocytosis. This protein is thought to be implicated in the evasion of host immune responses by Staphylococcus aureus, and thus, might be a candidate for vaccine development approaches to prevent severe S. aureus infections. S. aureus is responsible for nosocomial infections as well as a variety of human infections, such as food poisoning, toxic shock syndrome, endocarditis, septicemia, skin infections, soft tissue infections, and bone infections. It is also responsible for bovine and ovine mastitis. SpA typing or DNA sequence analysis of the variable repeat region of protein A gene is useful in determining S. aureus outbreak strains from those strains that are epidemiologically insignificant.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing sodium citrate
Preparation Note
Prepared from P 6031, coupled to biotin by an amide bond through an aminocaproyl spacer.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
M Balasch et al.
Journal of comparative pathology, 121(2), 139-148 (1999-07-16)
This report describes the experimental inoculation of conventional pigs with a tissue homogenate obtained from two pigs affected with postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS). Eight 2-month-old pigs were inoculated by the intranasal route, and two pigs were left as uninfected
Anil K Pal et al.
Biosensors, 10(10) (2020-09-30)
We report a novel self-referenced diffraction-based leaky waveguide (LW) comprising a thin (~2 µm) film of a photofunctionalisable hydrogel created by covalent attachment of a biotinylated photocleavable linker to chitosan. Streptavidin attached to the chitosan via the photocleavable linker was
spa typing method for discriminating among Staphylococcus aureus isolates: implications for use of a single marker to detect genetic micro- and macrovariation.
Koreen L et al
Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 42(2), 792-799 (2004)
Scott D Kobayashi et al.
mBio, 4(5), e00764-e00713 (2013-10-03)
Staphylococcus aureus is a prominent cause of human infections worldwide and is notorious for its ability to acquire resistance to antibiotics. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), in particular, is endemic in hospitals and is the most frequent cause of community-associated bacterial
M Graille et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(10), 5399-5404 (2000-05-11)
Staphylococcus aureus produces a virulence factor, protein A (SpA), that contains five homologous Ig-binding domains. The interactions of SpA with the Fab region of membrane-anchored Igs can stimulate a large fraction of B cells, contributing to lymphocyte clonal selection. To
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service