M7648
Anti-Myosin (Skeletal and Smooth) antibody produced in rabbit
whole antiserum
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
conjugate:
unconjugated
application:
IF
clone:
polyclonal
species reactivity:
animal, human
citations:
8
technique(s):
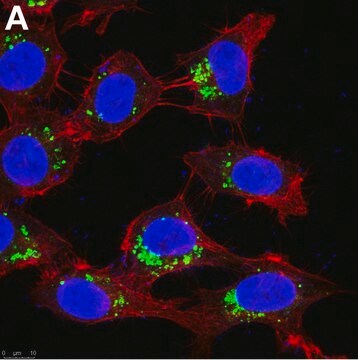
indirect immunofluorescence: 1:10 using cultured fibroblasts
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
whole antiserum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
contains
15 mM sodium azide
species reactivity
animal, human
technique(s)
indirect immunofluorescence: 1:10 using cultured fibroblasts
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... MYH10(4628) , MYH9(4627) , MYL9(10398)
Related Categories
General description
Myosin is a 500 kD protein that interacts with actin in muscle and in non-muscle cells. It is characterized with two identical heavy chains (200 kD each) and four light chains (15-20 kD each). Myosin molecules consist of two major regions; the tail (rod) and head. These molecules aggregate into filaments through the tail region and interact with actin and ATP through the head region.
Specificity
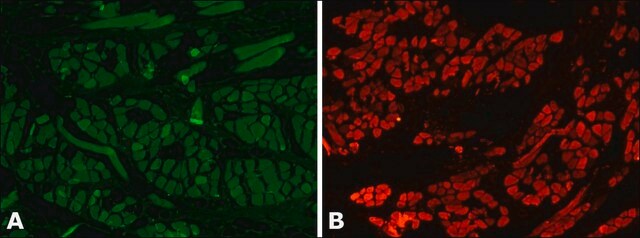
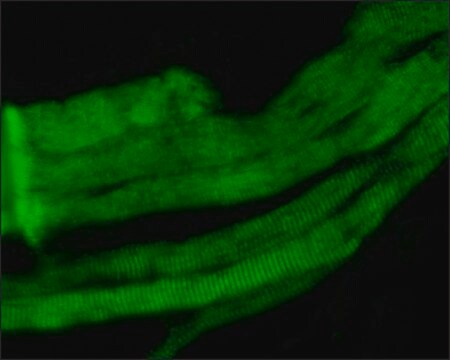
Shows a pattern of staining along stress fibers of cultured human and animal fibroblasts.
Immunogen
whole myosin (heavy and light chains) from bovine uterus.
Application
Anti-Myosin (Skeletal and Smooth) antibody produced in rabbit has been used in indirect immunofluorescence labeling.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Myosin plays a vital role in neurosensory and cortical function, membrane vesicle trafficking and determinant partitioning. Myosins with actin-stimulated ATPase activity is essential for various cellular movements. Myosins I and V mediates vesicle translocation. Myosin II with a long rod like tail domain, assembles into a bipolar thick filament and facilitate muscle contraction.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Anke Oertel et al.
Cell biology international, 27(12), 977-986 (2003-12-04)
Myosin was detected on Western blots of Micrasterias denticulata extracts by use of antibodies from different sources. Inhibitors with different targets of the actomyosin system, such as the myosin ATPase-blockers N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) and 2,3-butanedione monoxime (BDM), or the myosin light
Jenny Krönström et al.
Cell and tissue research, 336(2), 299-308 (2009-04-03)
Inside the light organs of the bioluminescent (light-producing) crustacean Meganyctiphanes norvegica (krill), numerous capillaries drain haemolymph into the light-producing structure (lantern). We have investigated the arrangement and function of filamentous material found around the opening of the capillaries. These have
Root hair formation: F-actin-dependent tip growth is initiated by local assembly of profilin-supported F-actin meshworks accumulated within expansin-enriched bulges
Baluska F, et al.
Developmental Biology, 227(2), 618-632 (2000)
Myosin: The Actin Motor Protein
Molecular Cell Biology, 10(1), 80-86 (2000)
Torsten Wollert et al.
The Journal of cell biology, 159(4), 571-577 (2002-11-20)
It is widely believed that microtubule- and F-actin-based transport of cytoplasmic organelles and membrane fusion is down-regulated during mitosis. Here we show that during the transition of Xenopus egg extracts from interphase to metaphase myosin V-driven movement of small globular
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service