A8678
Agar
suitable for plant cell culture
Synonym(s):
Agar-agar, Gum agar
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
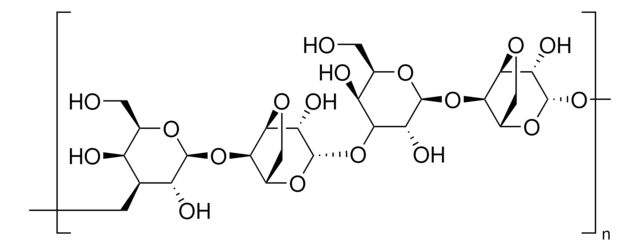
(C12H18O9)n
CAS Number:
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
50405901
NACRES:
NA.21
Recommended Products
biological source
algae (Rhodophyceae)
Quality Level
form
powder
technique(s)
cell culture | plant: suitable
mp
80-90 °C (1.5% in water)
transition temp
transition temp 27-37 °C (1.5%)
application(s)
agriculture
storage temp.
room temp
InChI
1S/C14H24O9/c1-5-8(16)13-11(7(21-5)4-20-13)23-14-10(18)12(19-2)9(17)6(3-15)22-14/h5-18H,3-4H2,1-2H3/t5?,6-,7?,8-,9+,10-,11?,12+,13+,14?/m1/s1
InChI key
GYYDPBCUIJTIBM-DYOGSRDZSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Agar or Agar-agar is one of the major components found in the cell wall of red algae. It is a polysaccharide complex, comprising about 70% agarose and 30% agaropectin.
Application
Washed agar has been used:
- as a supplement (0.9% w/v) to Murashige and Skoog basal medium for plant growth
- in the preparation of cocultivation medium for Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation in maize (Zea mays) hybrid Hi-II
- as a component in the complete medium to regenerate protoplasts of Piriformospora indica
- as a clean agar medium to culture Synechococcus WH7803 strain
Biochem/physiol Actions
Agar is an ester of sulfuric acid in a linear galactan form, that makes it soluble in hot water and insoluble in cold. Washed agar contain less impurities and low level of nutrients.
Preparation Note
Washed
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Alga Zuccaro et al.
Fungal genetics and biology : FG & B, 46(8), 543-550 (2009-04-09)
Piriformospora indica (Basidiomycota, Sebacinales) is a root colonizing fungus which is able to increase biomass and yield of crop plants and to induce local and systemic resistance to fungal diseases and tolerance to abiotic stress. A prerequisite for the elucidation
Andrew D Millard
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 501, 33-42 (2008-12-11)
Cyanophages are a group of viruses which specifically infect cyanobacteria. The cyanobacteria are predominantly aquatic phototrophic bacteria and the two dominant genera Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus contribute significantly to primary production in the oceans. Cyanophages that infect marine cyanobacteria were first
Arnaud Dechesne et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 74(16), 5195-5200 (2008-07-01)
Water is arguably the most important constituent of microbial microhabitats due to its control of physical and physiological processes critical to microbial activity. In natural environments, bacteria often live on unsaturated surfaces, in thin (micrometric) liquid films. Nevertheless, no experimental
Queeny Wing-Han Yuen et al.
The open biomedical engineering journal, 5, 39-46 (2011-06-07)
Cervical lymph nodes are common sites of metastatic involvement in head and neck cancers. These lymph nodes are superficially located and palpation is a common practice for assessing nodal hardness and staging cancer which is, however, too subjective and with
GunNam Na et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 286(47), 40423-40432 (2011-09-21)
When growing in its native habitat, Thlaspi goesingense can hyperaccumulate 1.2% of its shoot dry weight as nickel. We reported previously that both constitutively elevated activity of serine acetyltransferase (SAT) and concentration of glutathione (GSH) are involved in the ability
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service