396311
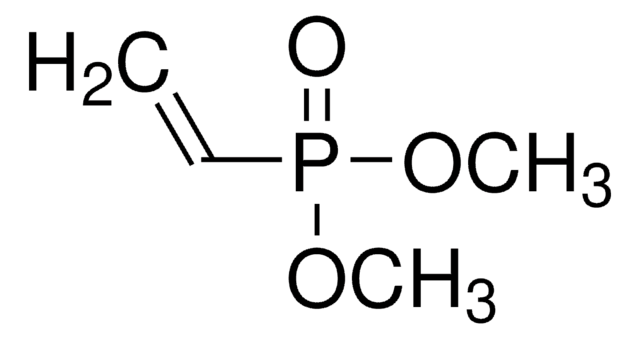
Vinylphosphonic acid
97%
Synonym(s):
p -Ethenylphosphonic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH2=CHP(O)(OH)2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
108.03
Beilstein:
1741622
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Assay
97%
mp
36 °C (Lit. dry VPA) (lit.)
density
1.37 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
OP(O)(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C2H5O3P/c1-2-6(3,4)5/h2H,1H2,(H2,3,4,5)
InChI key
ZTWTYVWXUKTLCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Vinylphosphonic acid (VPA) is an organophosphorus compound that is used in the surface treatment of metal substrates. It can be used in the preparation of poly(VPA) by radical polymerization in the presence of initiator systems and chain transfer agents. PVPA tends to have an electrolytic nature, which is useful for a variety of energy based applications.
Application
VPA based homopolymers and copolymers find usage in corrosion treatment, fuel cells, dental cement, drug delivery, and bio-mimicry.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Met. Corr. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
235.4 °F
Flash Point(C)
113 °C
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Anhydrous proton conducting polymer electrolytes based on poly (vinylphosphonic acid)-heterocycle composite material
Yamada M and Honma I
Polymer, 46(9), 2986-2992 (2005)
Polyphosphonate cements: a new class of dental materials
Ellis J and Wilson AD
Journal of Materials Science Letters, 9(9), 1058-1060 (1990)
Synthesis and characterization of functionalized poly (ε-caprolactone)
Wurth JJ and Shastri VP
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 51(16), 3375-3382 (2013)
Sadegh Rostamnia et al.
Journal of combinatorial chemistry, 11(1), 143-145 (2008-12-23)
Trisubstituted vinylphosphonates have been prepared via three-component reaction using phosphites, acetylenic esters, and aroyl chlorides in good yields. A variety of phosphites, activated acetylenes, and aroyl chlorides have been successfully employed in these reactions. In addition, three-component synthesis of vinylphosphonate
Stephan Salzinger et al.
Macromolecular rapid communications, 33(16), 1327-1345 (2012-07-11)
Recent studies have shown that poly(vinylphosphonate)s are readily accessible by rare earth metal-mediated group transfer polymerization (GTP). This article highlights the progress in this new field and advantages of GTP in comparison to classical anionic and radical polymerization approaches. Late
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service
![Bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/128/336/4e7a3e38-338c-423e-95b8-70d9d1f8e121/640/4e7a3e38-338c-423e-95b8-70d9d1f8e121.png)