246174
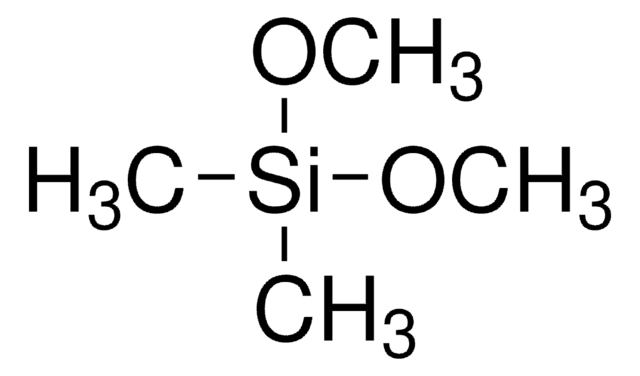
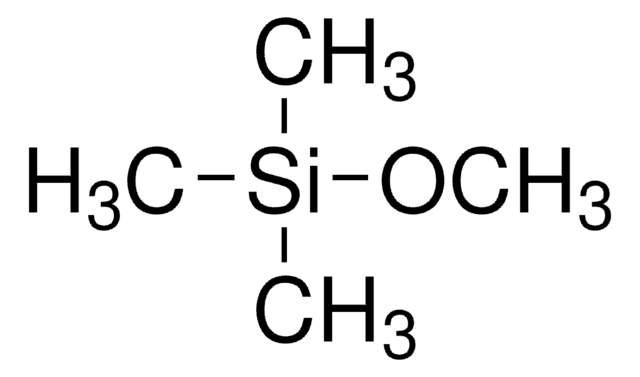
Trimethoxymethylsilane
98%
Synonym(s):
Methyltrimethoxysilane
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH3Si(OCH3)3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
136.22
Beilstein:
1736151
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352103
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.06
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
form
liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.371 (lit.)
bp
102-104 °C (lit.)
density
0.955 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CO[Si](C)(OC)OC
InChI
1S/C4H12O3Si/c1-5-8(4,6-2)7-3/h1-4H3
InChI key
BFXIKLCIZHOAAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Trimethoxymethylsilane (MTM) is an organosilicon compound widely used as a precursor for the preparation of silica-based materials, which finds the applications in various fields. Particularly in molecular assembly, linking nano building blocks, and selective synthesis oligosiloxane compounds. It can also be utilized as a crosslinker in the synthesis of polysiloxane polymers.
Application
Trimethoxymethylsilane can be used:
- As a silica source for synthesizing polyethyleneimine-silica (PEI-silica) organic-inorganic hybrid particles.
- To transform hydrophilic ceramic surfaces to hydrophobic by modifying the -OH groups.
- To modify silica aerogels by inducing hydrophobicity and enhancing mechanical properties without affecting transparency.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Liq. 2
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
48.2 °F
Flash Point(C)
9 °C
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
The formation of polyethyleneimine?trimethoxymethylsilane organic?inorganic hybrid particles.
Neville F, et al.
Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 431, 42-50 (2013)
Investigation of Silane Modified Ceramic Surface of Porous Mullite Ceramics.
Markovska I, et al.
World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 79(7), 272-276 (2013)
Organo-modified silica aerogels and implications for material hydrophobicity and mechanical properties.
Martin L, et al.
Journal of Materials Chemistry, 18(2), 207-213 (2008)
Utilization of alkoxysilyl groups for the creation of structurally controlled siloxane-based nanomaterials
Kuroda K, et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 26(1), 211-220 (2014)
Sameer Kulkarni et al.
Journal of chromatography. A, 1174(1-2), 50-62 (2007-11-21)
Sol-gel coating with covalently bonded low-molecular-weight (MW<300 Da) poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) chains was developed for capillary microextraction (CME). The sol-gel chemistry proved effective in the immobilization of low-molecular-weight PEGs thanks to the formation of chemical bonds between the organic-inorganic hybrid
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service