52738-U
Supelclean™ PSA SPE Bulk Packing
pkg of 100 g
Synonym(s):
PSA SPE material (primary secondary amine)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Agency
suitable for GB 5009.253-2016
Quality Level
product line
Supelclean™
feature
endcapped
packaging
pkg of 100 g
extent of labeling
8.4% C
3.3% N loading
technique(s)
solid phase extraction (SPE): suitable
surface area
500 m2/g
surface coverage
surface coverage 2.35 μmol/m2
matrix
silica gel base material (irregularly shaped)
matrix active group
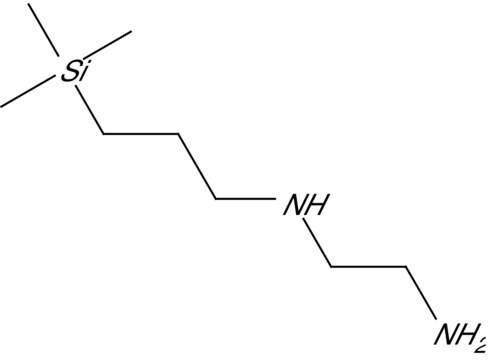
ethylenediamine-N-propy bonding
particle size
50 μm
pore size
70 Å pore size
pKa
(1) 10.1, (2) 10.9
capacity
0.98-1.05 meq/g capacity
application(s)
PFAS testing
food and beverages
separation technique
ion exchange
normal phase
General description
Sample Matrix Compatibility: Organic or aqueous solutions
- Polymerically bonded, ethylenediamine-N-propyl phase that contains both primary and secondary amines
- A weak anion exchanger with a pKa of 10.1 and 10.9
- Similar to aminopropyl SPE phases (NH2) in terms of selectivity, but has a much higher capacity due to presence of secondary amine (0.98-1.05 meq/g)
- Strong affinity and high capacity for removing fatty acids, organic acids, and some polar pigments and sugars when conducting multi-residue pesticide analysis in foods
- Has been shown to significantly reduce matrix-enhancement effects encountered during the GC analysis of food products
- Tested for superior cleanliness using GC-FID and GC-MS
- Bidentate nature of ligand allows for chelation
Application
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Inhalation
Target Organs
respiratory tract irritation
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
SPE retention mechanism in this case is based on the electrostatic attraction of charged functional groups of the analyte(s) to oppositely charged functional groups on the sorbent.
Protocols
Extraction and Analysis of Agricultural Pesticides from Oranges Using the “QuEChERS” Method
Retention occurs through polar interaction between the sorbent and analytes. Typical sample matrices that can be employed in normal-phase SPE include hydrocarbon or fatty oils diluted in a solvent like hexane, isooctane, chlorinated solvent, THF, diethyl ether, or ethyl acetate.
Related Content
Solid phase extraction purifies samples for chromatographic analysis, improving data quality and protecting analytical columns.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 52738-U | 4061835552160 |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service