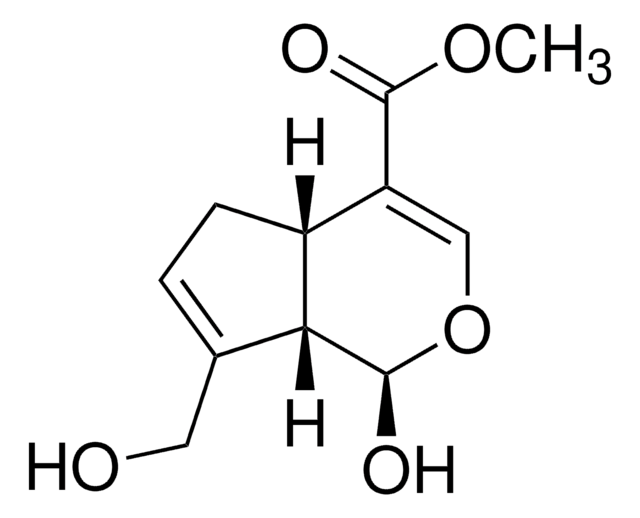
T5398
Transglutaminase from guinea pig liver
lyophilized powder, ≥1.5 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
Protein-Glutamine-γ-Glutamyltransferase, Protein-glutamine:amine γ-glutamyltransferase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
form
lyophilized powder
Quality Level
specific activity
≥1.5 units/mg protein
mol wt
76.6 kDa
composition
Protein, ≥80% modified Warburg-Christian
solubility
H2O: soluble 1.0 mg/mL, clear
application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
This product from Sigma has been used to demonstrate that tissue transglutaminase (tTG) selectively deamidates gluten peptides, which results in strongly enhanced T cell-stimulatory activity. It has also been used to assess immune responses to A-gliadin peptides. Furthermore, it has been used to demonstrate that tTG selectively modifies gliadin peptides that are recognized by gut-derived T cells in celiac disease.
Transglutaminase has been used in a study to improve quantifiable assays to fully characterize the role of transglutaminase in diseases such as Huntington′s disease and Alzheimer′s disease.Transglutaminase has also been used in a study to develop a nonradioactive dot blot assay for transglutaminase activity.
Biochem/physiol Actions
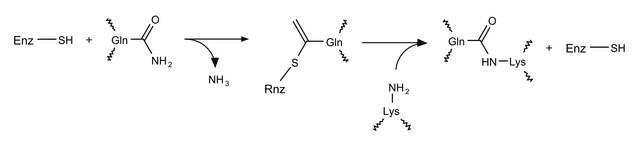
Transglutaminase from guinea pig liver consists of a single polypeptide chain of 691 amino acid residues. It has six potential glycosylation sites (Asn-X-Ser or Asn-X-Thr), but it is not glycosylated. The molecular mass is approximately 76.6 kDa. It is calcium dependent and has several calcium binding sites. The enzyme is inhibited by iodoacetamide and N-ethylmaleimide in the presence of calcium. It catalyzes the incorporation of small molecular weight amines into γ-glutamine sites of proteins. In the absence of small molecular weight amines, it catalyzes the cross linking of proteins that results in the formation of γ-glutamyl-ε-lysine side chain peptides. Liver transglutaminase is a nonzymogenic enzyme.
Unit Definition
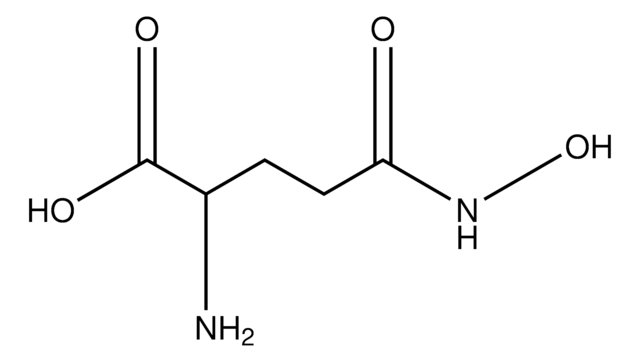
One unit will catalyze the formation of 1.0 μmole of hydroxamate per min from Nα-Z-Gln-Gly and hydroxylamine at pH 6.0 at 37 °C. (L-Glutamic acid γ-monohydroxamate is the standard.)
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing Tris and dithioerythritol
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
M P M Adriaanse et al.
Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics, 37(4), 482-490 (2013-01-08)
Enterocyte damage is the hallmark of coeliac disease (CD) resulting in malabsorption. Little is known about the recovery of enterocyte damage and its clinical consequences. Serum intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) is a sensitive marker to study enterocyte damage.
R P Anderson et al.
Nature medicine, 6(3), 337-342 (2000-03-04)
Celiac disease (CD) is an increasingly diagnosed enteropathy (prevalence, 1:200-1:300) that is induced by dietary exposure to wheat gliadins (as well as related proteins in rye and barley) and is strongly associated with HLA-DQ2 (alpha1*0501, beta1*0201), which is present in
Jessica C Kiefte-de Jong et al.
Gastroenterology, 144(4), 726-735 (2013-01-15)
Celiac disease in pregnant women has been associated with poor growth of the fetus, but little is known about how the level of celiac disease affects fetal growth or birth outcomes. We assessed the associations between levels of antibodies against
L Lorand et al.
Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 58(1-2), 9-35 (1984-01-01)
This paper is intended as a background to the topic of transglutaminases, while focusing on current ideas regarding the biological roles of these enzymes. Specifically, the following topics are discussed: geometry of forming gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine cross-linked structures; energetic considerations; the gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine
Mechanism of action of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme: identification of a functional cysteine essential for activity.
J E Folk et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 241(23), 5518-5525 (1966-12-10)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service