SAB4200865
Anti-Pro GDF11 antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
GDF11 Growth/differentiation factor 11 Bonemorphogenetic protein11 (bmp11)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.43
species reactivity:
mouse, rat
application:
technique(s):
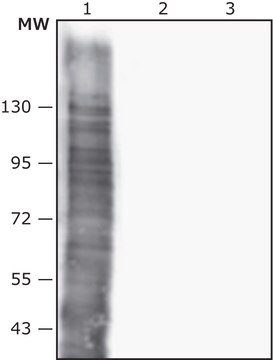
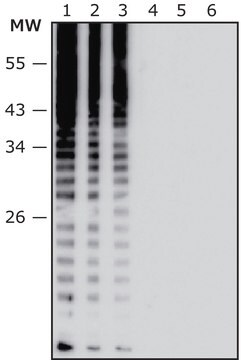
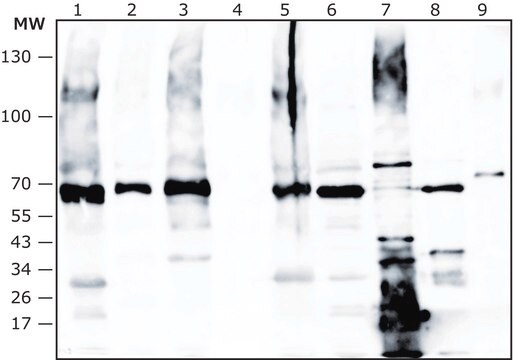
immunoblotting: 1:500-1:1000 using rat PC12 cell line
citations:
5
Recommended Products
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
Quality Level
form
liquid
species reactivity
mouse, rat
concentration
~1 mg/mL
technique(s)
immunoblotting: 1:500-1:1000 using rat PC12 cell line
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
Growth Differentiation Factor 11 (GDF11) is expressed in many tissues, including skeletal muscle, pancreas, kidney, nervous system, and retina, among others. GDF11 circulating levels and protein content in tissues are quite variable and are affected by pathological conditions or age.1 GDF11 also known as Bone Morphogenetic Protein 11 (BMP-11), mRNA is translated in a precursor protein, which is processed by specific proteases generating the mature GDF11 (C-terminal, 12.5 kDa) and the pro-domain (Nterminal, 30.1 kDa). GDF11 shares 89% amino acid sequence homology with GDF8, however GDF8 expression in human tissues is restricted to cardiac and skeletal muscle,2 while GDF11 is expressed in all tissues.3 Although there is high homology between mature GDF8 and GDF11, the pro-domains of both proteins share only 54% homology. The pro-domain is fundamental for proper protein folding, disulfide bond formation and exportation of the homodimers,4,5 suggesting differences in posttranslational process.
Specificity
Anti-Pro GDF11 antibody specifically recognizes Pro GDF11 from human origin.
Application
The antibody may be used in various immunochemical techniques including Immunoblotting. Detection of the Pro GDF11 band by Immunoblotting is specifically inhibited by the immunogen.
Biochem/physiol Actions
GDF11 uses the canonical receptors and the SMAD proteins for signaling. The GDF11 dimer (a disulfide-linked homodimer of carboxy-terminal fragments) binds the activin receptors type II A or B (ActRIIA, ActRIIB), proteins with serine/threonine kinase activity.
Physical form
Supplied as a solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide as a preservative.
Storage and Stability
For continuous use, store at 2-8°C for up to one month. For extended storage, freeze in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use. Working dilution samples should be discarded if not used within 12 hours.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
A M Gray et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 247(4948), 1328-1330 (1990-03-16)
Many proteins are initially synthesized as part of a large precursor. The role of the pro-region in the biosynthesis of transforming growth factor--beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and activin A, two structurally related disulfide-linked homodimers synthesized as large precursors, was studied.
Arturo Simoni-Nieves et al.
Frontiers in oncology, 9, 1039-1039 (2019-11-05)
Growth Differentiation Factor 11 (GDF11), a member of the super family of the Transforming Growth Factor β, has gained more attention in the last few years due to numerous reports regarding its functions in other systems, which are different to
Francesco S Loffredo et al.
Cell, 153(4), 828-839 (2013-05-15)
The most common form of heart failure occurs with normal systolic function and often involves cardiac hypertrophy in the elderly. To clarify the biological mechanisms that drive cardiac hypertrophy in aging, we tested the influence of circulating factors using heterochronic
Mathias Uhlén et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 347(6220), 1260419-1260419 (2015-01-24)
Resolving the molecular details of proteome variation in the different tissues and organs of the human body will greatly increase our knowledge of human biology and disease. Here, we present a map of the human tissue proteome based on an
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service