L8507
Luciferase from Vibrio fischeri (Photobacterium f)
lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Bacterial Luciferase, Luciferase from Photobacterium fischeri
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
Luciferase from Vibrio fischeri has been used in a study to assess kinetics of light emission and oxygen consumption by bioluminescent bacteria. It has also been used in a study to investigate the sensitivity of dark mutants of various strains of luminescent bacteria to reactive oxygen species.
Features and Benefits
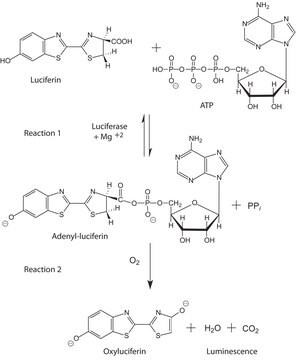
Partially purified, soluble extracts containing FMN-dependent luciferase and NADH- and NADPH-dependent FMN reductases. Produces light in a system containing FMN, NADH or NADPH, and n-decyl aldehyde.
Other Notes
ATCC No. 7744 balance primarily buffer salts and stabilizer.
Physical form
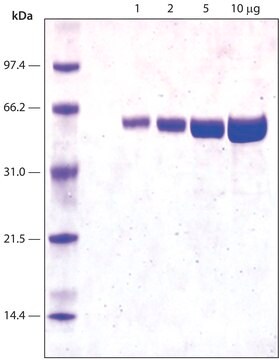
Partially purified lyophilized powder
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Patricia G Cruz et al.
Chemistry & biology, 18(11), 1442-1452 (2011-11-29)
The chemical diversity of nature has tremendous potential for the discovery of molecular probes and medicinal agents. However, sensitivity of HTS assays to interfering components of crude extracts derived from plants, and macro- and microorganisms has curtailed their use in
J J Bourgois et al.
Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes, 33(4), 353-363 (2001-11-17)
Oxygen plays a key role in bacterial bioluminescence. The simultaneous and continuous kinetics of oxygen consumption and light emission during a complete exhaustion of the exogenous oxygen present in a closed system has been investigated. The kinetics are performed with
Anya Bakhrat et al.
Cell biology and toxicology, 27(3), 227-236 (2011-03-03)
We describe a Saccharomyces cerevisiae bioluminescence assay for UV and arsenate in which bacterial luciferase genes are regulated by the promoter of the yeast gene, UFO1. UFO1 encodes the F-box subunit of the Skp1–Cdc53–F-box protein ubiquitin ligase complex and is
Ismael Rodea-Palomares et al.
Archives of environmental contamination and toxicology, 57(3), 477-487 (2009-01-27)
The bioavailability and therefore toxicity of a metal depends on the chemical species present in a particular environment. We evaluated the effect of a series of factors that could potentially modify metal speciation on the toxicity of Hg, Cu, Zn
M-L Foucault et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 76(1), 264-274 (2009-11-03)
Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) is emerging as a powerful tool for real-time monitoring of infections in living animals. However, since luciferases are oxygenases, it has been suggested that the requirement for oxygen may limit the use of BLI in anaerobic environments
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service