76512
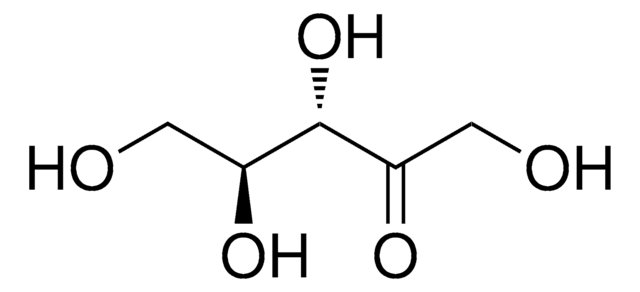
D-Ribulose solution
~1 M in H2O, ≥97.0% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
D-erythro-2-Ketopentose solution, D-erythro-2-Pentulose solution, D-Adonose solution, D-Arabinulose solution, D-Araboketose solution, D-Erythropentulose solution
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C5H10O5
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
150.13
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥97.0% (HPLC)
form
liquid
concentration
~1 M in H2O
color
colorless
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
OCC1(O)OC[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O
InChI
1S/C5H10O5/c6-2-5(9)4(8)3(7)1-10-5/h3-4,6-9H,1-2H2/t3-,4-,5?/m1/s1
InChI key
LQXVFWRQNMEDEE-ZZKAVYKESA-N
Biochem/physiol Actions
D-Ribulose is a metabolite in pentose and glucuronate interconversions. It plays a role in the D-arabitol production from U. fabae. Ribulose is a rare aldopentose that might show antitumoral and antiviral activities. It acts as a substrate for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+)-dependent D-arabitol dehydrogenase (ARD1p) enzyme and D-tagatose-3-epimerase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Its monophosphate D-ribulose 5-phosphate is an intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway of glycolysis. D-Ribulose may be found in plants like algae, sugar beet leaves, and barley seed leaves.
Packaging
Bottomless glass bottle. Contents are inside inserted fused cone.
Other Notes
To gain a comprehensive understanding of our extensive range of Monosaccharides for your research, we encourage you to visit our Carbohydrates Category page.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Tobias Link et al.
The Biochemical journal, 389(Pt 2), 289-295 (2005-03-31)
We have identified and characterized a novel NADP(+)-dependent D-arabitol dehydrogenase and the corresponding gene from the rust fungus Uromyces fabae, a biotrophic plant pathogen on broad bean (Vicia faba). The new enzyme was termed ARD1p (D-arabitol dehydrogenase 1). It recognizes
Kosei Takeda et al.
Acta crystallographica. Section F, Structural biology and crystallization communications, 64(Pt 10), 945-948 (2008-10-22)
D-Arabinose isomerase catalyzes the isomerization of D-arabinose to D-ribulose. Bacillus pallidus D-arabinose isomerase has broad substrate specificity and can catalyze the isomerization of D-arabinose, L-fucose, L-xylose, L-galactose and D-altrose. Recombinant B. pallidus D-arabinose isomerase was overexpressed, purified and crystallized. A
Ye-Wang Zhang et al.
Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 87(6), 1993-1999 (2010-05-25)
Recombinant Escherichia coli harboring the L: -arabinose isomerase (BLAI) from Bacillus licheniformis was used as a biocatalyst to produce L: -ribulose in the presence of borate. Effects of substrate concentration, the borate to L: -arabinose ratio, pH, and temperature on
Ye-Wang Zhang et al.
Preparative biochemistry & biotechnology, 40(1), 65-75 (2009-12-22)
Recombinant Escherichia coli whole cells harboring Bacillus licheniformis L-arabinose isomerase (BLAI) were harvested to prepare alginate-immobilized biocatalysts. The operational conditions for immobilization were optimized according to relative activity and the cell leakage of the immobilized cell. The optimal conditions are
Chakkiath Paul Antony et al.
International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology, 62(Pt 7), 1613-1618 (2011-09-06)
A moderately haloalkaliphilic methylotrophic bacterium possessing the ribulose monophosphate pathway for carbon assimilation, designated MPL(T), was isolated from Lonar Lake sediment microcosms that were oxidizing methane for two weeks. The isolate utilized methanol and was an aerobic, Gram-negative, asporogenous, motile
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service