W269808
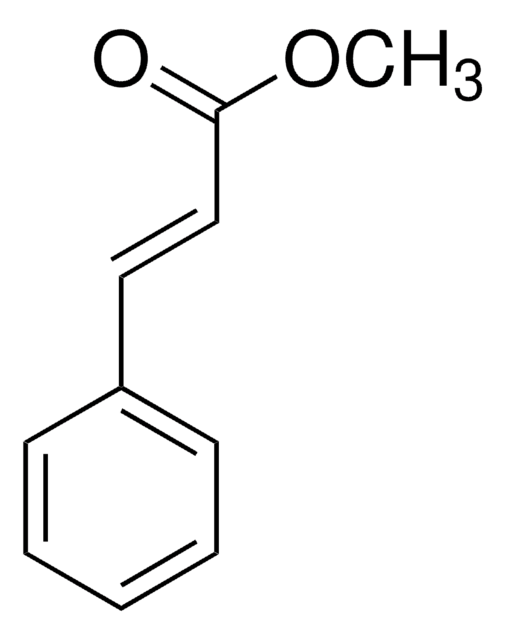
Methyl trans-cinnamate
≥98%, stabilized, FCC, FG
Synonym(s):
trans-Cinnamic acid methyl ester
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic
Quality Level
grade
FG
Halal
Kosher
Agency
meets purity specifications of JECFA
reg. compliance
EU Regulation 1334/2008 & 178/2002
FCC
Assay
≥98%
contains
alpha-tocopherol as stabilizer
bp
260-262 °C (lit.)
mp
34-38 °C (lit.)
application(s)
flavors and fragrances
Documentation
see Safety & Documentation for available documents
food allergen
no known allergens
Organoleptic
balsam; fruity; strawberry
SMILES string
COC(=O)\C=C\c1ccccc1
InChI
1S/C10H10O2/c1-12-10(11)8-7-9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h2-8H,1H3/b8-7+
InChI key
CCRCUPLGCSFEDV-BQYQJAHWSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service