Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation Protocols
What are Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells?
Adult somatic cells can be reprogrammed into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) with the overexpression of key reprogramming genes (OCT4, KLF4, SOX2, cMYC, NANOG and LIN28). Human iPSCs have the unique ability to differentiate into any cell type of the body including:
- Ectodermal: Neuron, Astrocyte, Oligodendrocyte, Retinal Epithelial Cell (RPE), Epidermal, Hair and Keratinocytes.
- Endodermal: Hepatocyte, Pancreatic β-islet Cell, Intestinal Epithelial Cell, Lung Alveolar Cells.
- Mesodermal: Hematopoietic, Endothelial Cell, Cardiomyocyte, Smooth Muscle Cell, Skeletal Muscle Cell, Renal cell, Adipocyte, Chondrocyte and Osteocytes.
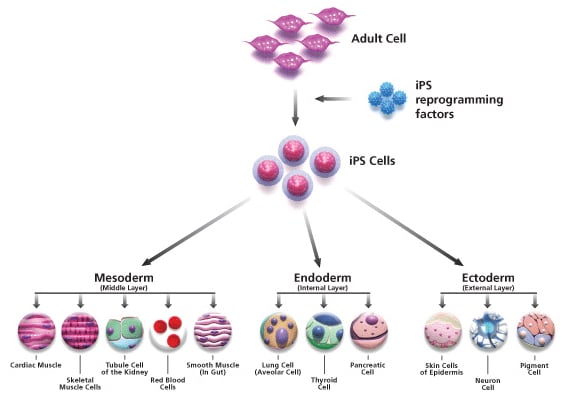
Figure 1.IPSC Pathway
iPSC Collection
We offer a large collection of cell culture media, supplements, bioactive small molecules, and growth factors used to control the cell fate of human iPSCs. The table below highlights the most widely used protocols, media and characterization antibodies used to differentiate human iPSC’s into different cell lineages.
Products
Loading
References
1.
Chambers SM, Fasano CA, Papapetrou EP, Tomishima M, Sadelain M, Studer L. 2009. Highly efficient neural conversion of human ES and iPS cells by dual inhibition of SMAD signaling. Nat Biotechnol. 27(3):275-280. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1529
2.
Shi Y, Kirwan P, Livesey FJ. 2012. Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to cerebral cortex neurons and neural networks. Nat Protoc. 7(10):1836-1846. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.116
3.
Ma L, Liu Y, Zhang S. 2011. Directed Differentiation of Dopamine Neurons from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.411-418. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-201-4_30
4.
Karumbayaram S, Novitch BG, Patterson M, Umbach JA, Richter L, Lindgren A, Conway AE, Clark AT, Goldman SA, Plath K, et al. 2009. Directed Differentiation of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Generates Active Motor Neurons. 27(4):806-811. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.31
5.
Shaltouki A, Peng J, Liu Q, Rao MS, Zeng X. 2013. Efficient Generation of Astrocytes from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Defined Conditions. 31(5):941-952. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1334
6.
Douvaras P, Wang J, Zimmer M, Hanchuk S, O’Bara M, Sadiq S, Sim F, Goldman J, Fossati V. 2014. Efficient Generation of Myelinating Oligodendrocytes from Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Patients by Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reports. 3(2):250-259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.06.012
7.
Burridge PW, Matsa E, Shukla P, Lin ZC, Churko JM, Ebert AD, Lan F, Diecke S, Huber B, Mordwinkin NM, et al. 2014. Chemically defined generation of human cardiomyocytes. Nat Methods. 11(8):855-860. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2999
8.
Maffioletti SM, Gerli MFM, Ragazzi M, Dastidar S, Benedetti S, Loperfido M, VandenDriessche T, Chuah MK, Tedesco FS. 2015. Efficient derivation and inducible differentiation of expandable skeletal myogenic cells from human ES and patient-specific iPS cells. Nat Protoc. 10(7):941-958. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.057
9.
Patsch C, Challet-Meylan L, Thoma EC, Urich E, Heckel T, O’Sullivan JF, Grainger SJ, Kapp FG, Sun L, Christensen K, et al. 2015. Generation of vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 17(8):994-1003. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3205
10.
Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Nagaoka M, Li J, Battle MA, Duris C, North PE, Dalton S, Duncan SA. 2010. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology. 51(1):297-305. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23354
11.
Zhang D, Jiang W, Liu M, Sui X, Yin X, Chen S, Shi Y, Deng H. 2009. Highly efficient differentiation of human ES cells and iPS cells into mature pancreatic insulin-producing cells. Cell Res. 19(4):429-438. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.28
12.
Huang SXL, Islam MN, O'Neill J, Hu Z, Yang Y, Chen Y, Mumau M, Green MD, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Bhattacharya J, et al. 2014. Efficient generation of lung and airway epithelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 32(1):84-91. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2754
Sign In To Continue
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?