GC Analysis of Aldehydes (PFBOA Derivatives) in Beer on SLB®-5ms after SPME using a 65 μm PDMS/DVB Fiber
Materials
analytical column
CONDITIONS
sample preparation
derivatization procedure: Add 100 μL of PFBOA solution (6 g/L) to 10 mL of deionized water in a 20 mL glass vial and seal. (Insert the PDMS/DVB SPME fiber in the headspace of the PFBOA solution for 10 min at 50 °C.)
sample/matrix
10 mL of degassed beer, 3.5 gm sodium chloride in 20 mL vial
SPME fiber
PDMS-DVB, 23 guage, 65 μm, Auto, Pk/3 (57345-U)
extraction
60 min, headspace, 50 °C, agitation (5 min on, 30 min off)
desorption process
0.10 min, 250 °C
column
SLB-5ms, 30 m x 0.25 mm I.D., 0.50 μm (28473-U)
oven
40 °C, 7 °C/min to 250 °C (14 min)
inj. temp.
250 °C
detector
MSD, SIM
MSD interface
275 °C
carrier gas
helium, 1.1 mL/min
injection
splitless
liner
0.75 mm I.D. SPME liner
sample
Beer
Description
Analysis Note
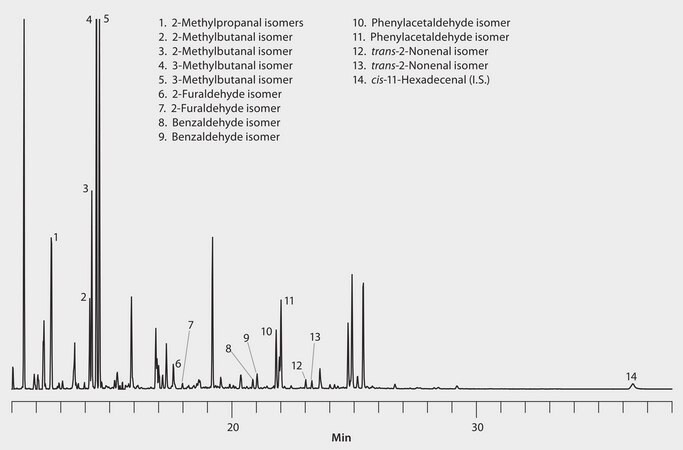
The formation of aldehydes is a major contributor to the deterioration in flavor or "staling" of beer upon storage. Research indicates that the source of these aldehydes is the type of malt used and quality of the wort produced during the brewing process. This application illustrates the use of SPME to extract aldehydes from beer, followed by on-fiber derivatization with 0-(2,3,4,5,6- pentafluorobenzyl)hydroxylamine hydrochloride (PFBOA). The aldehydes are then analyzed by GC/MS-SIM as their corresponding PFBOA derivatives. The aldehydes exist as geometric isomers, resulting in two derivatives for each. In the case of several of the analytes, these two derivatives were resolved chromatographically.
Legal Information
SLB is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany