Microbial Identification Tests & Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical, immunological, and molecular biological tests for microbial identification or the differentiation between groups of organisms are used regularly in microbiological quality control at production facilities and in academic research. Such microbial identification tests detect specific proteins, certain biochemical activities of the target cells (for example the activity of an enzyme), or gene sequences that are characteristic for microorganisms. Many microbial identification tests deliver important results within a short time, are very economical and user-friendly, and most do not need specific equipment or instrumentation. Some biochemical tests require only a drop of reagent to be applied on an agar plate or in a liquid medium.
Related Resources
- Article: Advantages of in situ hybridization over other microbial methods
Fast molecular screening of beverage, water, wastewater and food for microorganisms
- Whitepaper: Rapid Detection and Identification of Bacteria and Yeast
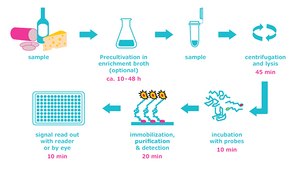
HybriScan® system is a new technology based on the detection of microbe-specific rRNA using sandwich hybridization. It allows comprehensive and reliable routine control of microbial contamination during food production, from raw materials to finished goods.
- Poster: Rapid Detection of Beer Spoilage Bacteria
Beer-spoiling microorganisms cause an increase of turbidity and unpleasant sensory changes in beer. Since the improved process technology in modern breweries has resulted in signifi cant reduction of oxygen content in the fi nal product, the role of strictly anaerobic bacteria like Pectinatus and Megasphaera has increased.
- Poster: Rapid Detection of Salmonella
Food-borne pathogens Salmonella is commonly evaluated in manufacturing of peanut butter and other food products. For the HybriScan®D Salmonella Test (Cat. No. 55662) the ISO based enrichment method is recommended.
- Brochure: HybriScan® Rapid Test System
When you need reliable routine control of microbial contamination in food production, from raw materials to finished goods, conventional standard cultivation-based methods are time consuming and often take from 2 to 15 days to get results.
- Brochure: ID Membranes for Rapid Microbial Identification
Growth on Petri dishes is usually the first step to identify microorganisms. Smart, inexpensive membranes can speed up the subsequent ID procedure to 1 to 4 hours.
- Brochure: Disks and Strips for Micobial Identification and Confirmation
Disks and Strips are very helpful for the identification and confirmation of microorganisms or to monitor sterilization. They are based on rapid methods, easy to use and a great value.
Biochemical reagents for identification
Biochemical reagents form the basis for liquid biochemical tests to detect, for example, an enzyme activity that is characteristic for a target microorganism. Such tests can often be performed directly on agar plates or liquid media.
Microscopy reagents & kits
Reagents and kits for staining microorganisms are used to differentiate and identify these under the microscope. Well-known tests like Gram staining help to give further biochemical, structural, or morphological information.
Microbiological testing kits
The test kits are based on different methods, including biochemical and immunological ones. The results can be evaluated by, for example, visible coagulation, a color reaction, or turbidity.
HybriScan® in situ hybridization
The advanced microbial identification system HybriScan® is a rapid molecular biology test for the accurate detection and identification of spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms in beverages, water, and food. It is based on in situ hybridization with probes. A robust test in a microtiter plate format, the microbial identification system does not require a thermocycler like a PCR test does.
Discs, strips, and identification membranes
Discs, strips, and ID membranes are among the many user-friendly microbial identification test formats based on biochemical reagents and reactions. The reagents are impregnated on a carrier, for example paper, and are therefore stable and easy to handle. A well-known example are the oxidase strips to check for cytochrome oxidase activity.
Related Webinars
Learn about the advantages, disadvantages, and costs of the HybriScan® method compared to common methods.
Related Videos
Video: How does in situ hybridization technology work?
The HybridScan® system is an in situ hybridization technology for spoilage organism testing in alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?