T3198
Monoclonal Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α antibody produced in mouse
clone 45418.111, purified immunoglobulin, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Anti-TNF-α
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
45418.111, monoclonal
form
lyophilized powder
species reactivity
rat
technique(s)
capture ELISA: suitable
neutralization: suitable
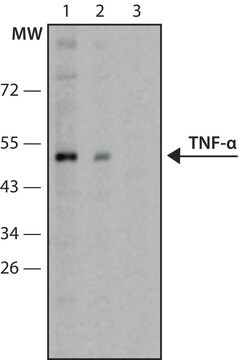
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL
isotype
IgG1
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
rat ... Tnf(24835)
General description
The antibody has the ability to neutralize the biological activity of rat TNF-α.and may also be used as a capture antibody in ELISAs.
Immunogen
purified recombinant rat TNF-α expressed in E. coli.
Application
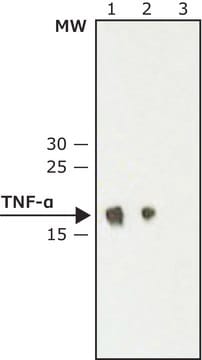
Monoclonal Anti-Tumor necrosis factor-α antibody produced in mouse has been used in immunoneutralization study and western blot analysis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) is a cytokine produced by macrophages in response to stimulus by LPS. It plays a major role in mediating inflammation, tissue injury, pathogenic shock, innate immunity, apoptosis and autoimmunity. The physiological effects of TNF-α are mediated by receptors of Tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) super family. TNF/TNFR also results in the activation of downstream pathways involving mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), p38(a class of MAPK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and NF-κB (Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) that play a major role in innate immunity, acute inflammatory responses and homeostasis.
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) affects various cellular processes such as blood-brain barrier, inflammatory, thrombogenic and vascular changes following brain damage. TNFα expression is upregulated in various central nervous system disorders, including Alzheimer′s disease, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson′s disease, meningococcal meningitis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Elevated expression of TNFα in the brain and blood in response to lipopolysaccharide might increase brain stem thrombosis, hemorrhage and stroke sensitivity/risk in hypertensive rats. Tumor necrosis factor-α activates polymorphonuclear leukocyte NADPH oxidase, thereby facilitates development of systemic oxidative stress (OS), inflammation and hypertension in rats.
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) affects various cellular processes such as blood-brain barrier, inflammatory, thrombogenic and vascular changes following brain damage. TNFα expression is upregulated in various central nervous system disorders, including Alzheimer′s disease, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson′s disease, meningococcal meningitis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Elevated expression of TNFα in the brain and blood in response to lipopolysaccharide might increase brain stem thrombosis, hemorrhage and stroke sensitivity/risk in hypertensive rats. Tumor necrosis factor-α activates polymorphonuclear leukocyte NADPH oxidase, thereby facilitates development of systemic oxidative stress (OS), inflammation and hypertension in rats.
Physical form
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in phosphate buffered saline containing carbohydrates.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Pallavi Shrivastava et al.
Journal of neuroinflammation, 14(1), 83-83 (2017-04-15)
Opioid receptors are known to control neurotransmission of various peptidergic neurons, but their potential role in regulation of microglia and neuronal cell communications is unknown. We investigated the role of mu-opioid receptors (MOR) and delta-opioid receptors (DOR) on microglia in
Effects of IFN-β1a and IFN-β1b treatment on the expression of cytokines, inducible NOS (NOS type II), and myelin proteins in animal model of multiple sclerosis.
Lubina-Dabrowska N, et al.
Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp., 65(4), 325-338 (2017)
Alleviation of hepatic steatosis accompanied by modulation of plasma and liver TNF- levels by Trigonella foenum graecum (fenugreek) seeds in Zucker obese (fa/fa) rats.
Raju J, and Bird R P
International Journal of Obesity, 30(8), 1298-1298 (2006)
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: a possible priming agent for the polymorphonuclear leukocyte-reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in hypertension.
Mazor R, et al
Hypertension, ;55(2), 353-362 (2010)
Mu-opioid receptor and delta-opioid receptor differentially regulate microglial inflammatory response to control proopiomelanocortin neuronal apoptosis in the hypothalamus: effects of neonatal alcohol.
Shrivastava P, et al.
Journal of Neuroinflammation, 14(1, 83-83 (2017)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service