G1546
Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) antibody, Mouse monoclonal
clone GSN149, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Synonym(s):
Mouse Anti-GFP
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.46
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified from hybridoma cell culture
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
GSN149, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
packaging
antibody small pack of 25 μL
technique(s)
indirect ELISA: suitable
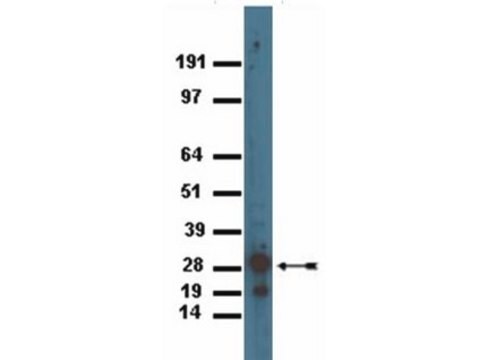
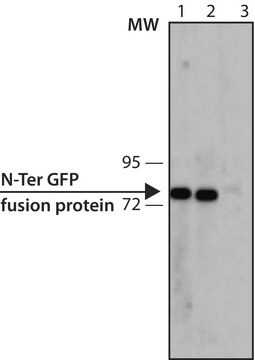
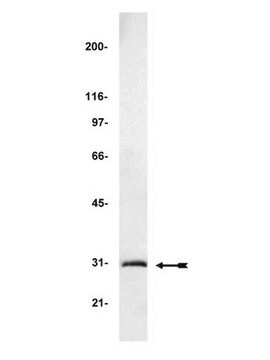
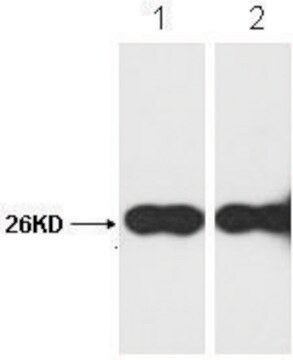
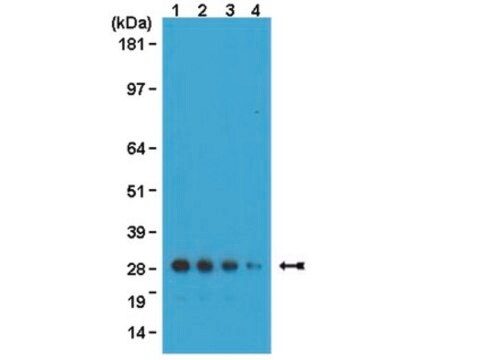
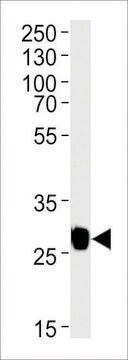
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL using extracts of cells expressing GFP fusion proteins
isotype
IgG1
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
Monoclonal Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the hybridoma GSN149 produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with a synthetic peptide of the Green fluorescent protein from jellyfish Aequorea victoria. GFP is a 27 kDa protein (238 amino acids) that can produce a strong green fluorescence without the need for a substrate. It absorbs light maximally at 395 nm and emits a bright green fluorescence with a peak at 509 nm. The GFP chromophore is formed through cyclization and oxidation of an internal tripeptide motif (Ser65, Gly69 and Tyr66).
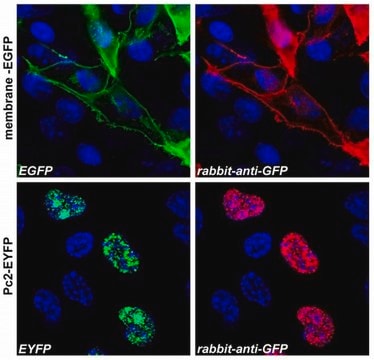
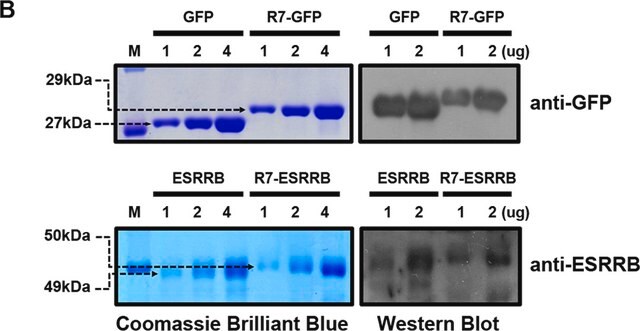
The antibody reacts specifically with GFP-fusion proteins.
Application
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Monoclonal Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) antibody produced in mouse was used in surface plasmon resonance (SPR) gold chip analysis to study the cysteine- and domain-mediated immobilization of enhanced GFP model protein.
Biochem/physiol Actions
GFP is implicated in protein detection and localization in living cells, as well as gene expression monitoring in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It detects protein-protein interactions in living cells.
Green fluorescent protein, produced in the jellyfish, Aequorea victoria, acts as secondary fluorescent protein in an energy transfer reaction to produce green light. It ability to produce a highly visible, internal fluorophore is widely applicable as marker for gene expression and to produce chimeric proteins to understand protein biochemistry.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
GFP: Lighting up life.
Martin Chalfie
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(25), 10073-10080 (2009-06-26)
Kyoungsook Park et al.
The Analyst, 136(12), 2506-2511 (2011-04-27)
Here we report an effective method for protein immobilization on a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) gold chip, describing the combination of cysteine- and oligomerization domain-mediated immobilization of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) as a model protein for the purpose of
The dynamic microbe: green fluorescent protein brings bacteria to light
Southward CM and Surette MG
Molecular Microbiology, 45(5), 1191-1196 (2002)
Visual screening of microspore-derived transgenic barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) with green-fluorescent protein
Carlson AR, et al.
Plant Cell Reports, 20(4), 331-337 (2001)
Annouck Luyten et al.
Molecular biology of the cell, 19(4), 1594-1604 (2008-02-08)
Wnt signaling pathways are essential for embryonic patterning, and they are disturbed in a wide spectrum of diseases, including cancer. An unresolved question is how the different Wnt pathways are supported and regulated. We previously established that the postsynaptic density
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service