About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Rosemarinus officinalis L.
form
powder
application(s)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
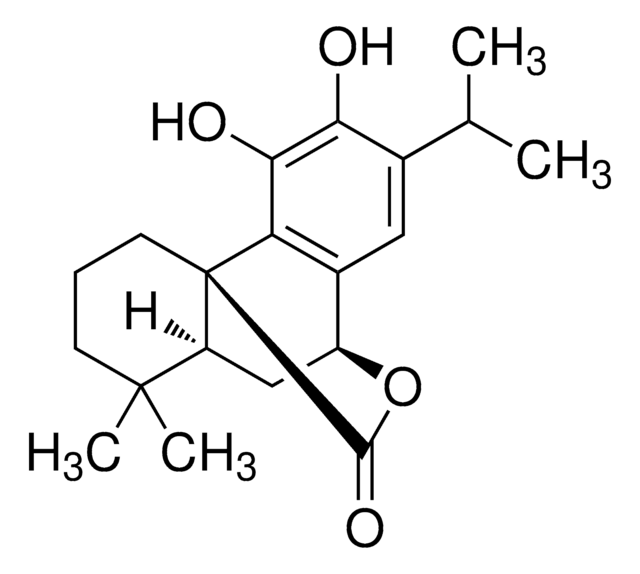
SMILES string
CC(C)c1cc2[C@@H]3C[C@H]4C(C)(C)CCC[C@]4(C(=O)O3)c2c(O)c1O
InChI
1S/C20H26O4/c1-10(2)11-8-12-13-9-14-19(3,4)6-5-7-20(14,18(23)24-13)15(12)17(22)16(11)21/h8,10,13-14,21-22H,5-7,9H2,1-4H3/t13-,14-,20+/m0/s1
InChI key
XUSYGBPHQBWGAD-PJSUUKDQSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- to test its anti-cancer and anti-proliferative activities on cancer stem-like cells (CSCs) and Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells
- to inspect its anti-carcinogenic effects on nineteen genes involved in up-and down-regulation of different genetic carcinogenesis pathways and on HeLa cells in human cervical cancer model
- as a reference standard to identify and quantify the metabolites of rosemary extract using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-MS/MS)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service