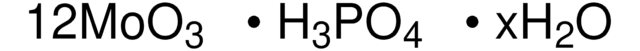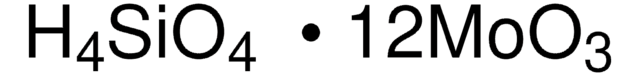431400
Phosphomolybdic acid hydrate
≥99.99% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Molybdophosphoric acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.99% trace metals basis
form
crystals
reaction suitability
reagent type: oxidant
impurities
≤0.01% insolubles
<100 ppm total metallic impurities
density
1.62 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤0.02%
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.025%
cation traces
Ca: ≤0.02%
Fe: ≤0.005%
NH4+: ≤0.01%
heavy metals: ≤0.005%
SMILES string
O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.O=[Mo](=O)=O.OP(O)(O)=O
InChI
1S/12Mo.H3O4P.H2O.36O/c;;;;;;;;;;;;1-5(2,3)4;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;/h;;;;;;;;;;;;(H3,1,2,3,4);1H2;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
InChI key
PDDXOPNEMCREGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- Catalysts for the nitration of aromatic compounds
- Highly dispersed MoOx/CNTs (carbon nanotubes) as a support for Pt catalysts
- Reduced molybdophosphate mixed-valence Keggin clusters
- Polyoxometalate (POM) hybrid materials based on Keggin polyanion building blocks
- Luminescent Langmuir-Blodgett films
- Anchored Wilkinson catalyst
Features and Benefits
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Ox. Sol. 3 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
5.1B - Oxidizing hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service